Why Is Earth’s Interior Hot?
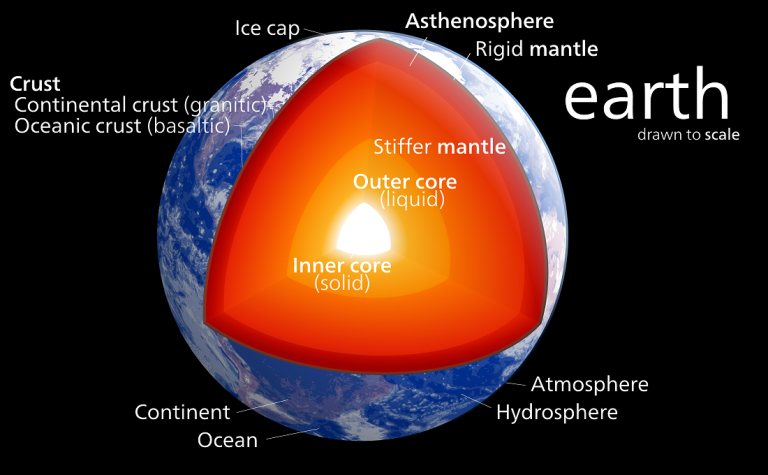
Earth’s interior is hot for several reasons. First, the Earth is composed of several layers, each with its own unique temperature. The inner most layer, the core, is the hottest part of the Earth and is estimated to have temperatures of up to 5,000°C. This heat is generated from the Earth’s formation, radioactive decay, and friction from the movement of the Earth’s tectonic plates. Additionally, heat is transferred from the Earth’s core to the outer layers through convection and conduction. This heat is then released from the surface in the form of volcanoes, hot springs, and geysers. Understanding why the Earth’s interior is hot is essential for predicting and understanding seismic activities, volcanoes, and other geologic phenomena.
The Earth’s Structure and Composition
Earth is composed of a variety of materials, including a solid inner core, a liquid outer core, and a solid crust. As we move further away from the Earth’s surface, the temperature and pressure increase. This hot interior is the result of several different processes that are all related to the Earth’s internal energy. The most significant source of heat is the decay of radioactive elements within the Earth’s mantle. This process releases a large amount of energy in the form of heat, which is transferred through the Earth’s mantle and core. Additionally, the Earth’s mantle is heated by gravitational forces and pressure from the overlying crust. This heat is then transferred through convection currents, which are driven by the Earth’s rotation. As a result, the Earth’s interior is constantly heated and the temperature increases with depth.
The Earth’s Heat Sources
:
Earth’s interior is much hotter than its surface, reaching temperatures as high as 6,000°C (10,832°F). This extreme heat has several sources, including the original heat of formation, radioactive decay, and the decay of gravitational energy.
The Earth’s original heat of formation came from the energy released when it was formed from a cloud of dust and gas about 4.5 billion years ago. This energy is still stored in the Earth’s core and mantle.
Radioactive decay is also responsible for heating up the Earth’s interior. The decay of certain elements, such as uranium, thorium, and potassium, releases radiation and heat over time. The amount of heat released by radioactive decay has decreased since the Earth formed, but it still accounts for a large portion of the Earth’s internal heat.
Finally, gravitational energy is released when material from the Earth’s interior moves toward the center of the planet. This material is very dense and releases a large amount of energy as it moves. This energy is then converted to heat.
These three sources combine to create the extreme temperatures found within the Earth’s interior. As the heat is released, it slowly moves toward the surface of the planet, where it is released and helps to create the Earth’s climate.
The Earth’s Heat Transfer
System
The Earth’s interior is hot due to heat transfer, which is the physical process by which thermal energy is exchanged between two objects or systems with different temperatures. Heat transfer can be divided into three main types: conduction, convection, and radiation. Conduction is the transfer of energy through a solid material, convection is the transfer of energy through a fluid, and radiation is the transfer of energy through electromagnetic waves. All three processes are responsible for transferring heat energy from the Earth’s core to its surface.
The primary source of the Earth’s internal heat is the energy released by the decay of radioactive elements. This energy is transferred from the Earth’s core to its mantle and crust through conduction and convection. The convection process is a continuous cycle of hot material rising from the deeper layers of the Earth, cooling off at the surface, and sinking back to the deeper layers. This cycle helps keep the Earth’s interior hot by constantly transferring energy from its core to its surface.
Radiation is also a major source of heat transfer in the Earth. Heat energy from the Earth’s core is transferred through electromagnetic waves, like infrared and ultraviolet radiation, to the Earth’s surface, resulting in the warming of the atmosphere. The radiation process is an important factor in climate change, as it helps regulate the temperature of the Earth’s atmosphere.
The Earth’s heat transfer system is a complex and dynamic process that is constantly at work in our planet. Heat is continuously transferred from the Earth’s core to its surface, and radiation plays a major role in this process. Understanding how this system works is key to understanding climate change and the Earth’s environment.

The Earth’s Heat Retention
Capacity
Earth’s interior is hot due to its incredible ability to store heat. This heat retention capacity is enabled by the planet’s natural insulation from the sun’s rays and the consistent production of heat-generating geothermal energy. When the sun’s energy is absorbed by the surface of the Earth, it is naturally insulated from the cooler outer layers of the atmosphere. This insulation traps the heat energy inside, causing the planet’s core temperature to rise over time. This stored heat energy is also released through the process of geothermal energy, which is the production of energy from the Earth’s internal heat. This process is responsible for the volcanoes, geysers, and hot springs found in various places around the planet. Additionally, the Earth’s interior is hot because of the internal friction generated by the gradual movement of its tectonic plates. This tectonic activity produces heat energy, which is then stored and released gradually, making the Earth’s interior hot.
The Earth’s Heat Gradient
is an incredibly fascinating phenomenon to explore. The interior of the Earth is immensely hot, and it is not due to a furnace at the core of the planet. In fact, it is the result of a few processes that create a gradual increase in temperature as you move away from the Earth’s surface. Knowing the reasons behind this phenomenon is essential for understanding how the Earth works.
The Earth’s increasing temperature is largely due to the slow decay of radioactive elements, such as uranium, thorium, and potassium, which release energy as they decay. This energy, as well as the energy from the Earth’s formation, is then transferred to the surrounding rocks and minerals through the process of conduction. The radioactive elements are also the source of the Earth’s magnetic field, which helps to protect the planet from dangerous solar radiation.
In addition to the slow decay of radioactive elements, the Earth’s heat gradient is also affected by the gravitational force of the planet, which causes the rocks and minerals to become denser as they move away from the Earth’s surface. This means that the deeper you go beneath the surface, the more pressure the rocks are under, and the hotter they become. The high temperatures and pressures at the Earth’s core also contribute to the planet’s magnetic field.
The Earth’s Heat Gradient is a complex phenomenon, and understanding it is essential in order to gain a better understanding of the planet. By studying the origin of the Earth’s heat, scientists are able to gain insights into the planet’s formation, its structure, and its potential for future tectonic activity. It is also important to note that the Heat Gradient is a necessary part of the planet’s ecosystem, as it helps to regulate the global climate and has an impact on the distribution of water around the world. Understanding the Earth’s Heat Gradient is key in order to develop a better understanding of the planet and its environment.
The Earth’s Heat Impact
on Human Life
Earth’s interior heat has a profound effect on human life. The Earth’s core is composed of molten iron and other metals, and the immense pressure from the surrounding layers creates a vast amount of heat at Earth’s center. This heat radiates outwards, driving tectonic activity, creating volcanoes, and creating and maintaining the Earth’s climate system.
The Earth’s interior heat also affects the availability of resources. Heat from Earth’s core is the primary source of energy for hot springs and geysers, and it is also used in geothermal energy production. This heat is also used to heat homes and buildings, and it can be used to power industrial processes.
Earth’s interior heat is also responsible for the formation of minerals and metals. Heat from Earth’s core causes chemical reactions that create and release new elements, which are then available for use by humans. This heat also helps to form the metals and minerals that are essential for modern life, such as copper, iron, and aluminum.
The Earth’s interior heat also has a profound effect on the climate. The heat from Earth’s core helps to drive the Earth’s climate system, and it is responsible for the formation of clouds, wind, and precipitation. The Earth’s climate system is essential for life on Earth, as it helps to regulate temperatures and provide necessary moisture to plants and animals.
Earth’s interior heat is essential for human life, as it provides energy, resources, and regulates the climate. Without the Earth’s interior heat, life on Earth would be drastically different, and humans would have to find alternative sources of energy and resources. Therefore, it is important to recognize the importance of Earth’s interior heat and its impact on human life.
FAQs About the Why Is Earth’s Interior Hot?
1. What is the source of the heat inside the Earth?
A: The Earth’s interior is heated by the decay of radioactive elements, such as uranium, thorium, and potassium, which release energy in the form of heat as they undergo natural radioactive decay.
2. How does heat from the Earth’s interior escape?
A: The heat from the Earth’s interior is able to escape through convection. As the hot material from the Earth’s interior rises, it cools and sinks back down, which creates a convection current that carries the heat toward the surface.
3. How does the heat from the Earth’s interior affect the surface?
A: The heat from the Earth’s interior is responsible for many of the Earth’s natural features, such as volcanoes and geysers. The heat also causes the Earth’s plates to move, which is what causes earthquakes and other geological events.
Conclusion
Earth’s interior is hot because of the radioactive decay of elements found within the Earth’s core. This heat is released in the form of thermal energy and is the main source of energy for all of Earth’s geologic processes, including the movement of tectonic plates and the formation of mountains and volcanoes. This heat also drives the Earth’s internal engine, which is responsible for the creation of convection currents that help to transfer heat energy from the Earth’s core to its surface. Without the heat generated from this internal engine, the Earth would be a cold and lifeless place.