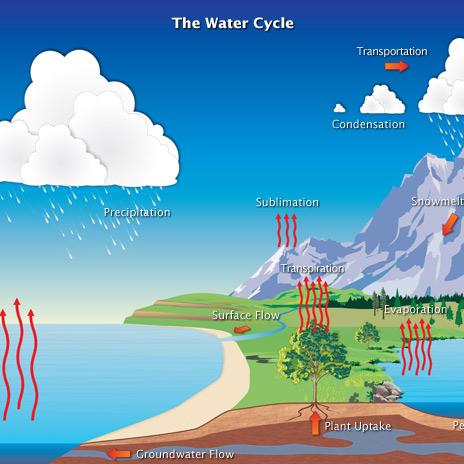
Which is Part of the Convection Cycle in Earth’S Atmosphere
The convection cycle is one of the most important processes in Earth’s atmosphere. It is responsible for transferring heat and energy from the surface of the planet to the upper atmosphere. The convection cycle occurs when warm air rises and cooler air sinks.
This process creates a circulation pattern that helps to distribute heat and energy around the globe.
The answer is simple: the sun. The sun is the driving force behind the convection cycle in Earth’s atmosphere. The heat from the sun warms the air near the surface of the planet, causing it to rise.
As it rises, it expands and cools, eventually reaching a point where it is cooler than the air around it and begins to sink back down toward the surface. This sinking air displaces the warmer air above it, which then begins to rise once again. The result is a continuous cycle of rising and falling air that drives our weather patterns.
Which is Part of the Convection Cycle in Earth’s Atmosphere Apex
The Apex is the highest point in Earth’s atmosphere. It is located in the stratosphere and extends from about 50 km to 85 km above Earth’s surface. The Apex is characterized by very low temperatures and high levels of ultraviolet radiation.
This region of the atmosphere is also home to the ozone layer, which protects life on Earth from harmful UV rays.
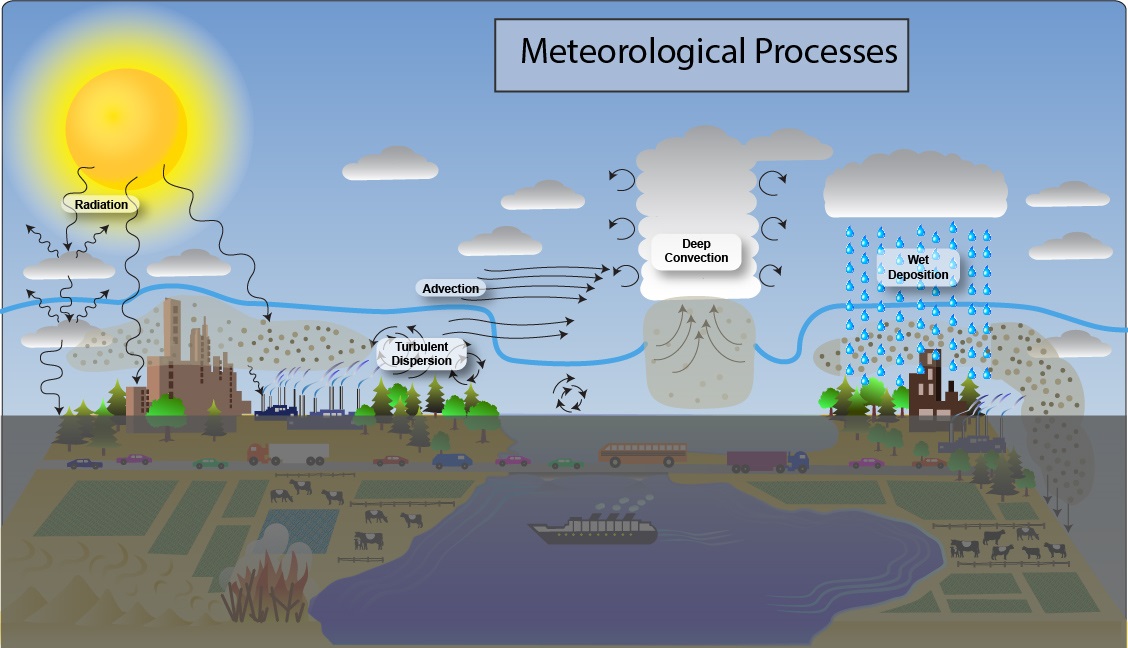
Credit: www.epa.gov
Which Happens is Part of the Convection Cycle in Earth’s Atmosphere?
The convection cycle in Earth’s atmosphere is a result of the sun heating the ground, which in turn heats the air above it. The hot air rises and expands, while the cooler air sinks and contracts. This creates a circulating pattern of airflow that drives the atmospheric circulation cells. The entire process is powered by differential heating, with the warm air rising and the cold air sinking.
What Does Convection Do in the Atmosphere?
Convection is the process of heat transfer by the mass motion of a fluid such as air or water. – The atmosphere is heated from below by the Earth’s surface, which is warmer than the air above it. The warm air rises and the cooler air sinks, creating convection currents in the atmosphere.
These convection currents help to distribute heat around the planet and play an important role in weather patterns.
Why Does the Convection Cycle Occur in the Atmosphere?
The air near the Earth’s surface is heated by the sun. This warm air rises and expands due to the lower pressure at higher altitudes. As the warm air rises, it cools and condenses into clouds.
The cooled air then sinks back down towards the surface, creating a convection current. This cycle repeats itself over and over again, causing winds to blow around the planet.
Why Does the Earth Have 3 Convection Cells?
The sun is the main source of energy for the earth’s atmosphere and oceans. The sun heats the earth’s surface, which in turn heats the air and ocean waters. The heated air and water rise, while cooler air and water sink.
This convection creates three cells in each hemisphere: the Hadley cell, Ferrel cell, and Polar cell. The Hadley cell forms at the equator where warm air rises. As this air rises, it expands and cools, causing it to sink back down towards the surface at about 30 degrees latitude.
This circulation pattern repeats itself creating a band of clouds around the equator known as the Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ). The Ferrel cell forms between the Hadley cell and the Polar cell at about 50-60 degrees latitude. In this region, rising air is deflected by Earth’s Coriolis Effect towards the west; at the same time, sinking air from higher latitudes moves in to replace it.
Polar cells form over Earth’s poles where cold air sinks back down to Earth’s surface. These cells are much weaker than Hadley or Ferrel cells because there is less difference in temperature between Earth’s equator and poles.
Astronomy – Ch. 9.1: Earth’s Atmosphere (29 of 61) The Daily Warming Cycle: Part 1
Conclusion
The Convection Cycle is one of the most important processes in the Earth’s atmosphere. It drives the weather and climate by moving heat and moisture around the planet. The cycle begins with the sun heating the surface of the earth.
This warm air rises and expands, becoming less dense than the cooler air around it. The rising air creates a low-pressure area at the surface, which sucks in more air from around it. This incoming air is warmed by the sun and rises, starting the cycle over again.