How Old Is Heliocentrism?
Heliocentrism is the scientific belief that the sun is at the center of the solar system and that all other objects in the universe orbit around it. It is one of the most fundamental theories in astronomy and has been accepted by most scientists since the 16th century. However, the idea of a sun-centered universe has been around for centuries before then, and there is evidence to suggest that heliocentrism was first suggested by ancient Greek philosophers. Despite this, it wasn’t until the 16th century that the scientific community accepted the idea as fact. Today, heliocentrism is the basis of modern astronomy and is accepted as fact in most scientific circles. The age of heliocentrism is difficult to determine, as it has been around in some form or another for thousands of years.
Historical Overview of Heliocentrism
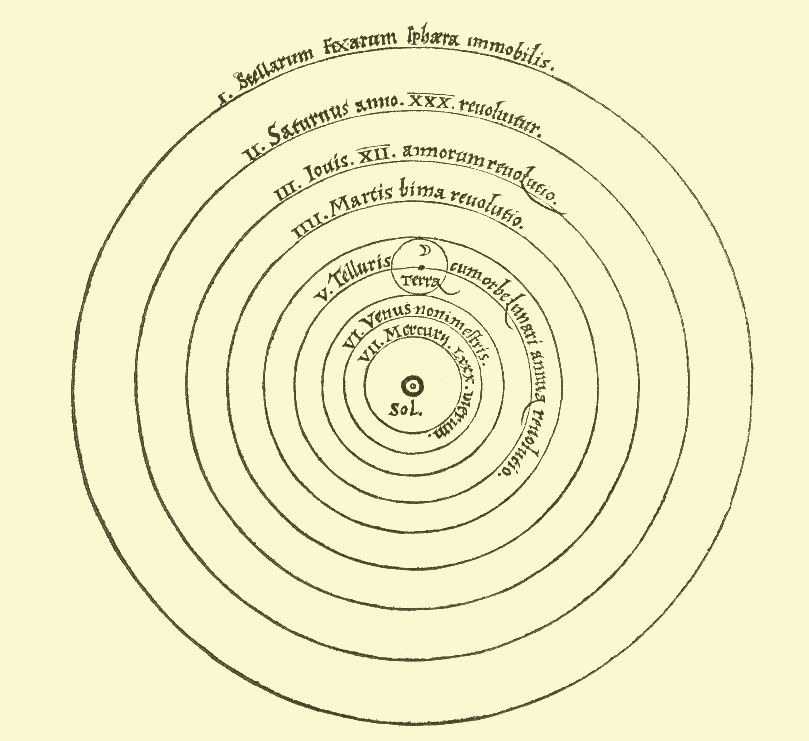
Heliocentrism is an astronomical model which states that the Sun is at the center of the universe and that all other bodies, such as planets, stars, and galaxies, orbit around it. Its origin dates back to ancient Greek philosophers such as Aristarchus of Samos and Plato, but it was not until the 16th century that heliocentrism gained widespread acceptance.
The 16th century saw a scientific revolution that introduced new theories and thought processes, and heliocentrism was one of them. The most notable figures in the advancement of this model include Nicolaus Copernicus, Johannes Kepler, and Galileo Galilei. Copernicus, in his book De Revolutionibus Orbium Coelestium (1543), proposed a heliocentric model of the universe that placed the Sun at the center. Kepler, in his book Astronomia Nova (1609) further advanced the heliocentric model by introducing elliptical orbits and Kepler’s laws of planetary motion. Finally, Galileo Galilei, in his book Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems (1632), provided the necessary evidence to support the heliocentric model, leading to its widespread acceptance.
Today, heliocentrism is the accepted model of the universe and is still used to accurately predict the motion of celestial bodies in space. Through continued research, heliocentrism has been refined and more evidence has been gathered to further support its accuracy.
The Evolution of Heliocentrism
Heliocentrism is the theory that the Sun is the center of the universe and that the planets, including Earth, revolve around it. The concept has been around since ancient times and has evolved over the centuries. Heliocentrism was first proposed by Aristarchus of Samos in the third century BCE. He believed that the Sun was a thousand times larger than Earth and that it was the center of the universe. However, this idea was not accepted by the scientific community until the sixteenth century, when Nicolaus Copernicus proposed that the planets revolved around the Sun. This concept was further developed by Johannes Kepler and Galileo Galilei, who both provided evidence that supported the heliocentric model.
Today, heliocentrism is an accepted scientific fact and is still being used to inform our understanding of the universe. It has been instrumental in our ability to explore the Solar System and has helped us develop theories about the formation of the planets and their orbits. Through the centuries, heliocentrism has been refined and improved upon, allowing us to gain a deeper understanding of our place in the universe.
The Impact of Heliocentrism on Modern Astronomy
Heliocentrism, the idea that the Sun is at the center of our Solar System, has had a profound impact on the development of modern astronomy. The concept was first proposed by Nicolaus Copernicus in the early 16th century, but it was not until the 17th century that it gained acceptance. Since then, heliocentrism has become the cornerstone of our understanding of the universe. Its impact has been so significant that it is considered one of the most significant scientific discoveries of all time.
The concept of heliocentrism has allowed astronomers to more accurately measure the distances between celestial bodies. This has allowed us to understand the size of our Solar System more accurately. Additionally, it has allowed us to make predictions about the orbits of planets in our Solar System, as well as measure the speed of light. By understanding heliocentrism, we can also better understand how the universe works and the forces that drive it.
Heliocentrism has also allowed us to understand the nature of stars and galaxies. By knowing the position of the Sun relative to other stars, astronomers have been able to better understand the age and size of stars, as well as their distances from the Earth. This has allowed us to gain insight into the evolution of the universe and the formation of galaxies.
Heliocentrism has been an invaluable tool in the development of modern astronomy. By understanding the concept, we can gain a greater understanding of the universe and its evolution. The impact of heliocentrism on modern astronomy cannot be overstated, and it is a concept that will continue to shape our understanding of the universe for the foreseeable future.

Heliocentrism and the Scientific Revolution
are often associated together, but how old is the heliocentric model? Heliocentrism is the astronomical model in which the Earth and the planets revolve around a stationary Sun. The theory was first proposed by the ancient Greek astronomer, Aristarchus of Samos, in the 3rd century BC.
The heliocentric model of the universe was further explored by other ancient astronomers, such as Ptolemy, Copernicus, and Galileo. However, it wasn’t until the 16th century when the heliocentric model of the universe was widely accepted by the scientific community. This was largely due to the work of Galileo and his advocacy for the Copernican model of the universe. He famously wrote a book, Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems, which was published in 1632.
Galileo’s work was a major breakthrough in understanding the heliocentric model of the universe, and it had a significant impact on the scientific revolution. His work was instrumental in the development of modern astronomy, and his advocacy for heliocentrism helped to overturn centuries of geocentric beliefs.
Since then, heliocentrism has become a staple of modern astronomy, and it is now widely accepted by the scientific community. While the exact age of heliocentrism is unclear, it is believed to be around 2,300 years old, making it one of the oldest theories in modern astronomy.
Overall, heliocentrism is a fundamental concept in modern astronomy and it has been an integral part of the scientific revolution. Its roots can be traced back to Aristarchus of Samos in the 3rd century BC, and it has since been accepted by the scientific community for over 400 years. It is a powerful reminder of how far we have come in understanding the universe and the role of the Sun at the center of our solar system.
The Reception of Heliocentrism Throughout History
Heliocentrism, the idea that the Sun is the center of the universe and that the planets revolve around it, dates back to ancient Greek times. But it wasn’t until the 16th century that the idea was accepted and embraced by the scientific community. This is when Nicolaus Copernicus, a Polish astronomer, wrote his revolutionary book, On the Revolutions of the Celestial Spheres, which proposed that the Sun is the center of the universe. This revolutionary work was met with skepticism and resistance from the church, but it eventually gained acceptance and heliocentrism became the accepted model of the universe.
In the 17th century, Galileo Galilei and Johannes Kepler further developed and refined Copernicus’ theory, providing tangible evidence for the heliocentric model. With Galileo’s astronomical observations and Kepler’s laws of planetary motion, heliocentrism was firmly established as the accepted view of the universe. This view was further strengthened by Isaac Newton’s discovery of the laws of gravity, which provided a mathematical explanation for how the planets orbit the Sun.
Today, heliocentrism is accepted as the scientific view of the universe and is taught in classrooms around the world. Although heliocentrism is centuries old, it is still being refined and tested by modern astronomers and physicists. The concept of heliocentrism is a testament to the power of scientific inquiry and the ability of humans to challenge and test accepted ideas.
Contemporary Scientific Views on Heliocentrism
Heliocentrism is the scientific theory that the sun is the center of the universe and that all other heavenly bodies move around it. This idea dates back to the ancient Greeks, and its influence on the scientific community and the world at large continues to this day. To better understand the age of this concept, we must look at the modern scientific views on heliocentrism.
In the 17th century, Johannes Kepler proposed that the sun was the center of the universe and that the planets revolve around it. This theory was later refined by Isaac Newton who proposed that the sun was the center of the solar system and all the planets revolved around it. While this was initially met with skepticism, it eventually became widely accepted within the scientific community.
Today, heliocentrism is considered to be a fundamental part of modern astronomy. While scientists have since discovered that the universe is far more complex than what was proposed by Kepler and Newton, the heliocentric model still provides a useful framework for understanding the motion of the planets. In addition, it is still used in space exploration, as well as in the search for extraterrestrial life.
Thus, heliocentrism is an ancient scientific concept that continues to be relevant today. It is a theory that is constantly being refined and improved, and its impact on the world has been remarkable. It is safe to say that heliocentrism is as old as science itself.
FAQs About the How Old Is Heliocentrism?
1. What is heliocentrism?
Answer: Heliocentrism is the scientific theory that the Sun is at the center of the Solar System and that the planets, including Earth, orbit around it.
2. Who proposed heliocentrism?
Answer: The first person to propose the idea of heliocentrism was Nicolaus Copernicus in the 16th century.
3. How old is heliocentrism?
Answer: Heliocentrism is approximately 500 years old, having been proposed by Nicolaus Copernicus in the 16th century.
Conclusion
Heliocentrism is an ancient scientific concept that has been around since the time of ancient Greek and Babylonian astronomers. Although it was not fully understood and accepted until the Copernican revolution of the 16th century, its basic principles were known by many ancient cultures. Today, heliocentrism is an accepted scientific theory that helps us understand the motions of the planets and other objects in the universe.