How is Energy Transferred from the Sun to the Earth
The sun is a star that is located at the center of our solar system. It is huge and so bright it’s hard to look at it with your eyes. The sun produces energy in the form of light and heat.
This energy travels through space and eventually reaches Earth. Once the energy reaches Earth, it is transferred to the atmosphere and then to the surface of the planet.
Energy Transfer from the Sun to the Earth – GCSE Physics lesson
The sun is the Earth’s primary source of energy. Solar radiation transfers energy from the sun to the Earth, where it is then used to power many of our planet’s natural processes. This includes everything from photosynthesis in plants to ocean currents and weather patterns.
Solar radiation consists of electromagnetic waves that travel through space at the speed of light. When these waves reach the Earth’s atmosphere, some of the energy is scattered or reflected back into space while some of it is absorbed by the atmosphere and land surface. The amount of energy that is scattered or reflected depends on various factors, such as cloud cover, atmospheric conditions, and the angle at which the sun’s rays strike the surface.
Once solar radiation reaches the Earth’s surface, it is transferred to the atmosphere and oceans through a process called convection. Convection is when warmer air rises while cooler air sinks. This creates circulation patterns in both the atmosphere and oceans that help redistribute heat around our planet.
How is Heat Transferred from the Sun to the Earth
The sun is the star at the center of our solar system and it is huge. It contains more than 99% of all the mass in our solar system. The sun is so large that it could fit about 1 million Earths inside of it.
The sun produces an enormous amount of energy every second. In fact, the sun produces more energy in one second than we humans have used in our entire history! The sun is a giant ball of gas and it is incredibly hot.
The temperature at the center of the sun can be as high as 15 million degrees Celsius! That’s about 27 times hotter than the surface of lava from a volcano. Even though space is a vacuum and there’s no air on the sun, it still has winds blowing across its surface at speeds up to 400 kilometers per hour!
How does all this heat and energy get from the sun to us here on Earth? Well, it travels through space in waves called electromagnetic radiation. This type of radiation doesn’t need anything like air or water to travel through—it can move through a vacuum just fine.
Electromagnetic radiation from the sun hits Earth’s atmosphere and warms it up. Some of this radiation bounces back out into space, but some penetrate all the way through the atmosphere to Earth’s surface. Once this radiation reaches Earth’s surface, it starts heating things up!
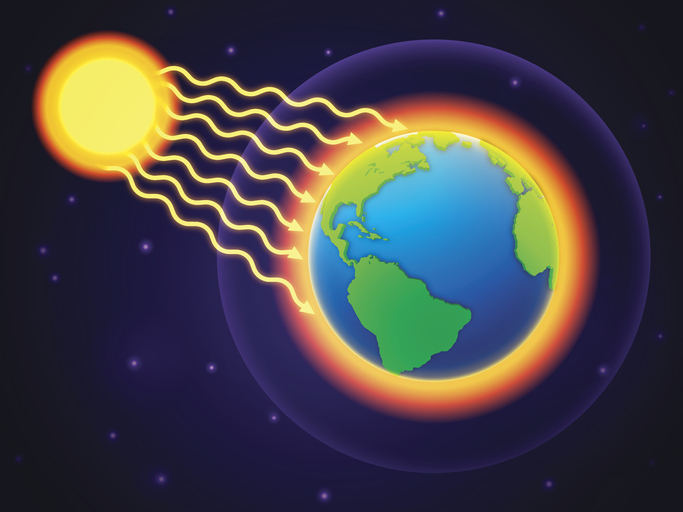

Credit: letstalkscience.ca
How is Energy Transferred from the Sun to the Earth
The sun is a star that is located at the center of our solar system. It is huge and so bright it’s hard to look at it with your eyes. The sun produces energy in the form of light and heat.
This energy travels through space and eventually reaches Earth. When the sun’s energy reaches Earth, some of it is reflected back into space while some of it is absorbed by our atmosphere. The atmospheric gases absorb some of the sun’s energy and re-emit it in all directions, both towards the surface of Earth as well as back out into space.
So not all of the sun’s energy makes it to Earth’s surface – some of it gets sent back out into space. The amount of sunlight that actually makes it through our atmosphere and reaches Earth’s surface varies depending on things like time of day, weather, seasons, etc. When sunlight hits Earth’s surface, it warms up the land and water which then radiates this heat upwards into the atmosphere in the form of infrared radiation.
Some greenhouse gases in our atmosphere (like water vapor, carbon dioxide, and methane) absorb this infrared radiation and trap heat in the atmosphere causing what we call the “greenhouse effect.” This trapped heat makes Earth warm enough for us to live on!
What Types of Energy Does the Sun Transfer to the Earth
When the sun’s rays hit the Earth’s atmosphere, they transfer energy in the form of heat and light. This energy is then transferred to the surface of the Earth, where it is eventually radiated back into space. The vast majority of the sun’s energy is transferred to the Earth in the form of visible light.
This light hits the Earth’s atmosphere and is scattered in all directions. Some of this light reaches the ground directly, while some of it is reflected off clouds or other objects before reaching the ground. In addition to visible light, the sun also emits ultraviolet (UV) radiation.
UV radiation makes up a small portion of sunlight, but it can have a big impact on living things. UV radiation can cause skin damage and eye problems, and it can also contribute to global warming.
How Does This Process Affect Our Planet And Its Climate
The greenhouse effect is a natural process that helps to regulate the Earth’s temperature. The Earth’s atmosphere traps some of the Sun’s energy, which makes the Earth’s surface warmer than it would be if there was no atmosphere. This trapped energy is what we call the greenhouse effect.
Without the greenhouse effect, the Earth would be too cold for life as we know it. But because of human activity, like burning fossil fuels and cutting down forests, we are making the greenhouse effect stronger. This is causing our planet to warm up at an unprecedented rate, which scientists say is changing our climate.
Climate change refers to a broad array of environmental degradation that is predicted to result from increasing levels of atmospheric CO2, including global warming, alterations in precipitation, sea level changes, and more extreme weather events. Climate change has the potential to severely damage our planet and its climate. It threatens public health and safety, food security, water resources, coastal areas, ecosystems, and biodiversity. And it could displace people around the world on a scale never seen before in history.
Conclusion
The sun is the source of all life on Earth. It is the largest object in our solar system and its huge mass makes it very dense. The sun’s gravity pulls everything towards it, including planets like Earth.
The sun has a huge amount of energy, which it produces through nuclear fusion. This energy is released as light and heat and travels across space to reach us. When this light and heat hits Earth’s atmosphere, some of it is reflected back into space while the rest passes through the atmosphere and reaches the surface of the planet.
At the surface, the energy is absorbed by things like water, rocks, and land masses. This energy then gets transferred around Earth through a process called convection. Warm air rises while cooler air sinks, causing a circulation of air that helps to even out temperatures around the globe.
Finally, this heated air reaches Earth’s poles where it cools down and sinks back towards the equator, completing the cycle.