Which Layer of the Earth is the Least Dense
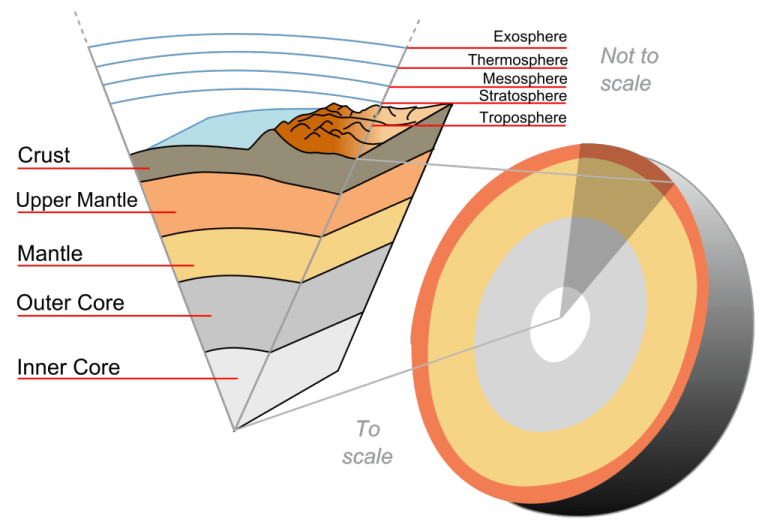
The crust is the outermost layer of the Earth and is also the thinnest. The average thickness of the crust is about 30 kilometers. Below the crust is the mantle, which is much hotter and more dense than the crust.
The mantle makes up about 84% of Earth’s volume. The core is the innermost layer of Earth and is made up of iron and nickel. It is very hot and under immense pressure. The core makes up about 16% of Earth’s volume.
The mantle is the layer of the Earth that lies between the crust and the core. It is the largest layer of the Earth, and also the least dense. The mantle is made up of hot, solid rock.
It is about 2,900 kilometers (1,800 miles) thick and makes up about 84% of the Earth’s total volume. The mantle is divided into two main parts: the upper mantle and the lower mantle. The upper mantle is cooler and harder than the lower mantle.
It is also less dense than the lower mantle. The lower mantle is hotter and softer than the upper mantle. It is also denser than the upper mantle.
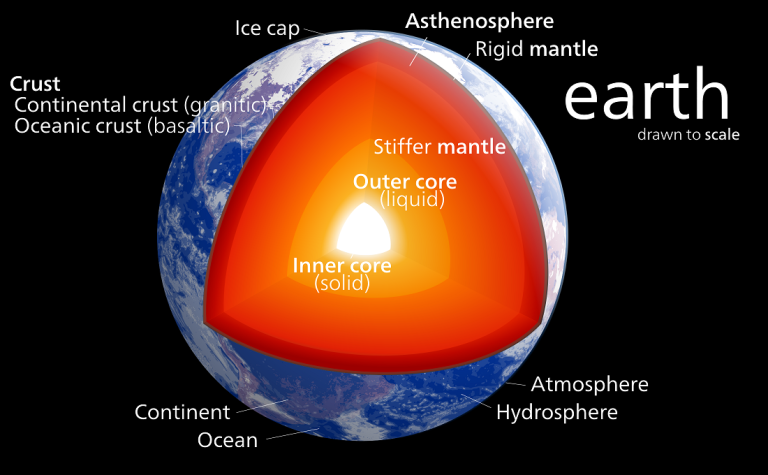
The lithosphere is a thin, outer layer that consists of both the crust and the uppermost part of the mantle. This layer sits on top of the asthenosphere, which is a hot flowy layer below it. The lithosphere is broken into tectonic plates that move around on top of the asthenosphere—this interaction between them drives plate tectonics and causes Earthquakes.
The Earth’s layers are not all equal in density—in fact, there’s quite a bit of variation! The least dense layer by far is the atmosphere, which consists mostly of nitrogen gas and other light gases like oxygen and carbon dioxide. Below that is the hydrosphere, which includes all of Earth’s water—ocean water, ice, groundwater, etcetera.
Next comes the mantle, as we just discussed, followed by the core. Finally, at the near-surface of the Earth (crust plus very shallow bits of the mantle), rocks are generally less dense than deep down in either the mantle or core.
What is the Least Dense Layer of the Earth’s Atmosphere
Atmospheric density is often described as a measure of the mass of the atmosphere per unit volume. It’s usually expressed in units of grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm^3). The least dense layer of the Earth’s atmosphere is the thermosphere.
This layer starts at an altitude of about 80 km and extends upward to about 800 km. The thermosphere is very thin, with a typical atmospheric density of only around 10^-4 g/cm^3. This makes it the lightest layer of the atmosphere, and also the easiest to escape from.
The thermosphere is where most satellites orbit, as it’s free from the drag that affects lower layers.

Credit: www.newsweek.com
What are Earth’S Layers from Most Dense to Least Dense?
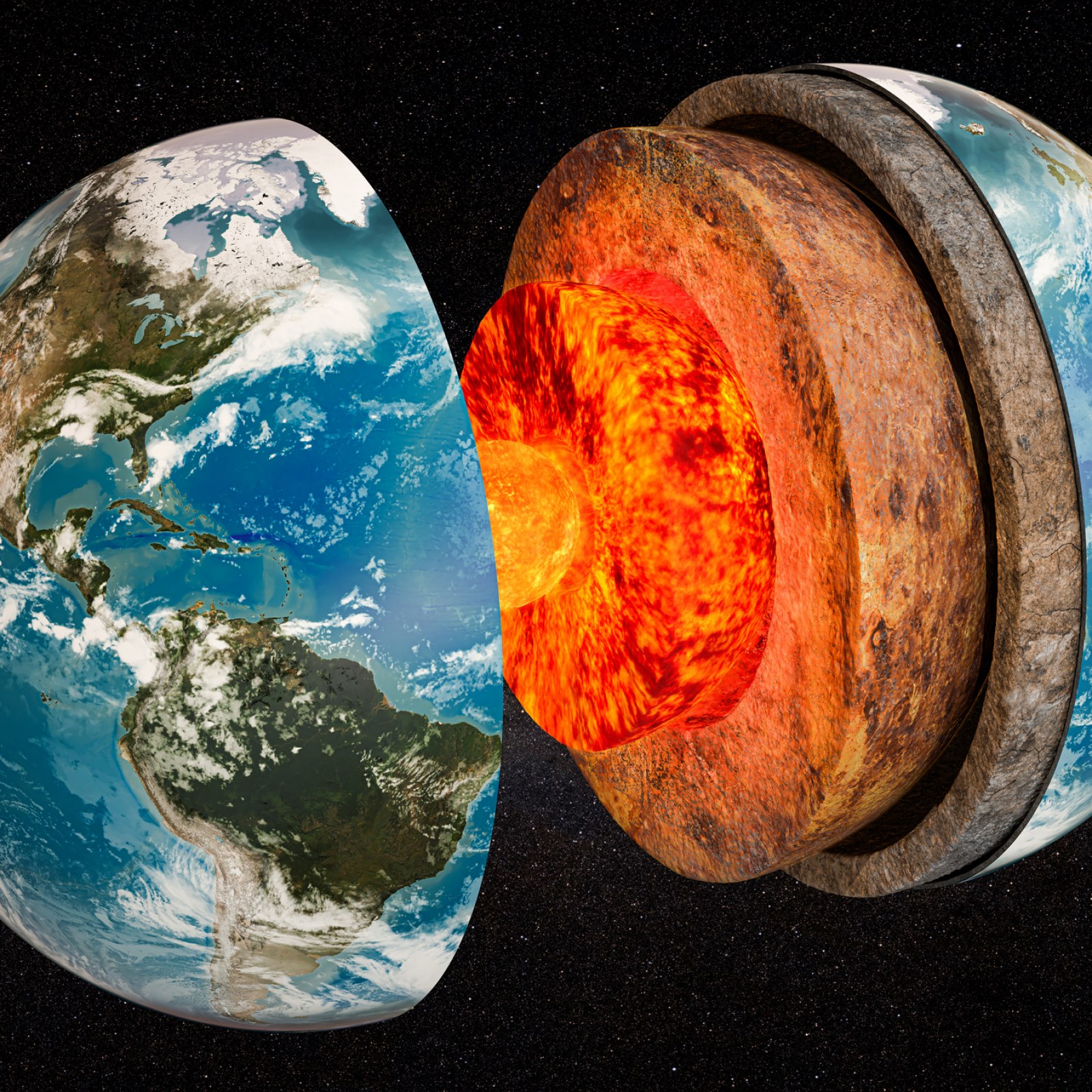
There are four main layers of the Earth: the inner core, outer core, mantle, and crust. The inner core is the most dense layer, followed by the outer core, mantle, and crust in order of increasing density. The inner core is a solid sphere of iron and nickel that has a diameter of about 1250 km.
It is under immense pressure from the overlying layers and has a temperature of around 5000 C. The high temperature and pressure cause the iron to be in a liquid state. The outer core is also made up of iron and nickel, but it is in a molten state due to the lower temperature (4000 C) and pressure. It has a thickness of about 2200 km.
The mantle is composed of silicate rocks that are rich in magnesium and iron. It has a thickness of 2900 km and makes up 83% of Earth’s volume. The mantle is divided into two regions: the upper mantle (or asthenosphere) and the lower mantle.
The asthenosphere is hotter and more fluid than the lower mantle, which is cooler and more rigid. The crust sits on top of the mantle and consists of less-dense rocks such as granite. The continental crust averages 40 km in thickness while the oceanic crust averages only 5-10 km thick.
What is the 2 Least Dense Layer of the Earth?
The two least dense layers of the Earth are the crust and the mantle. The crust is made up of solid rock and is a thin, outer layer that sits on the Earth’s molten mantle. The mantle is made up of hot, dense rock and is the layer below the crust. These two layers make up the Earth’s lithosphere, which is broken into tectonic plates.
Why is the Earth’s core so dense?
Conclusion
The Earth’s crust is the outermost layer of the Earth. It is a thin, rocky layer that is about 10 kilometers (6 miles) thick. The crust is made up of two types of rocks: igneous and sedimentary.
Igneous rocks are formed when molten rock (magma) cools and solidifies. Sedimentary rocks are formed from pieces of other rocks that have been broken down by wind, water, or ice. The mantle is the middle layer of the Earth.
It is a thick layer of rock that extends from the crust to a depth of 2,900 kilometers (1,800 miles). The mantle is made up of two types of rock: igneous and metamorphic. Igneous rocks are formed when molten rock (magma) cools and solidifies.
Metamorphic rocks are formed from other rocks that have been changed by heat and pressure deep within the Earth. The core is the innermost layer of the Earth. It is a dense layer of metal that extends from the mantle to a depth of 6,370 kilometers (3,960 miles).
The core consists mostly of iron with small amounts of nickel and sulfur.