Which Alkaline Earth Metal Has the Highest Electronegativity
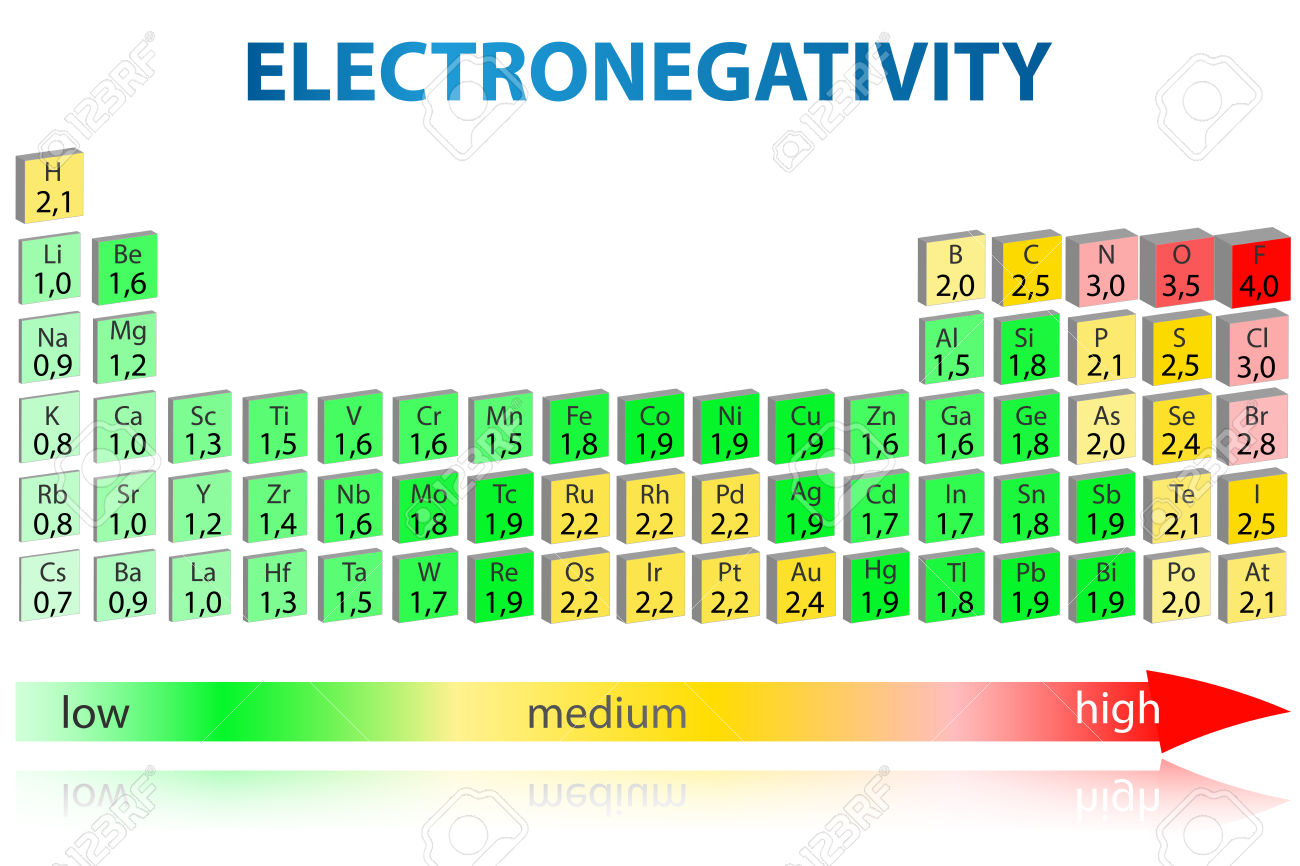
The electronegativity of an atom is a measure of how strongly it attracts electrons to itself. The higher the electronegativity of an atom, the more it will pull electrons away from other atoms. The alkaline earth metals are all highly electropositive, meaning they have a low electronegativity.
However, there is some variation among the alkaline earth metals in terms of their electronegativities. The most electronegative alkaline earth metal is beryllium, with an electronegativity of 1.57 on the Pauling scale. This means that beryllium is more than twice as electronegative as magnesium, which has an electronegativity of only 0.65.
Beryllium’s high electronegativity is due to its small size; because beryllium atoms are so small, they can easily hold onto electrons tightly. This makes beryllium atoms very good at forming covalent bonds with other atoms.
Which has the highest electronegativity? | 11 | S-BLOCK GROUP 2 – ALKALINE EARTH METALS | CHEMIS…
Alkaline earth metals are found in the second column of the periodic table and include magnesium, calcium, strontium, barium, and radium. These elements have high electronegativity values, meaning they easily form bonds with other atoms. The alkaline earth metal with the highest electronegativity is Radium.
Radium is a radioactive element that was first discovered in 1898 by Marie Curie and Pierre Curie. It has an atomic number of 88 and an atomic mass of 226.0 g/mol. The element is silvery white in color and is highly reactive.
It forms compounds with most elements, but it does not occur naturally in its pure form. Radium’s high electronegativity is due to its small size and high nuclear charge. This combination makes it difficult for electrons to remain stable in Radium atoms, so they tend to be pulled away by other atoms when forming bonds.
As a result, Radium atoms typically form covalent bonds with other atoms rather than ionic bonds. The high electronegativity of Radium makes it useful for some applications but also poses some dangers. For example, radium-based compounds are used in self-luminous paints and glassware because they emit light when exposed to radiation.
However, these same properties make radium dangerous if ingested or inhaled, as it can cause cancerous tumors to develop (which is why radium-based products are now regulated).
Which Member of the Alkaline Earth Metal Has the Smallest Electronegativity
The alkaline earth metals are a group of six chemical elements in the periodic table. All of the alkaline earth metals have low electronegativities. The element with the smallest electronegativity is beryllium, with an electronegativity of 1.57 on the Pauling scale.
Beryllium is followed by magnesium (1.73), calcium (1.00), strontium (0.95), barium (0.89), and radium (0.82).
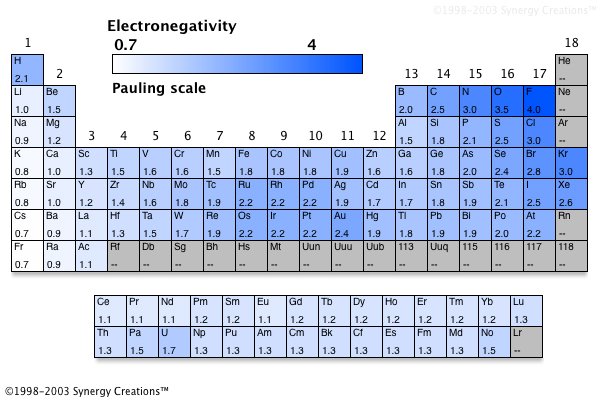
Credit: socratic.org
Do Alkaline Earth Metals Have High Electronegativity?
The electronegativity of an atom is a measure of how strongly it attracts electrons to itself. The higher the electronegativity of an atom, the more it will pull electrons away from other atoms. Alkaline earth metals generally have low electronegativities.
This is because they have low ionization energies, meaning they don’t hold on to their electrons very strongly. Additionally, alkaline earth metals have only two valence electrons (in their outermost energy level), so there isn’t a lot for them to attract in the first place. There are some exceptions to this general rule.
For example, beryllium has a higher electronegativity than magnesium because it is smaller and its valence electrons are closer to the nucleus. Additionally, some elements in the Lanthanide series (lanthanum, cerium, etc.) have high electronegativities due to having filled d orbitals which hold on to their electrons tightly.
Which Atom in the Alkaline Earth Metals Will Have the Greatest Electronegativity?
The alkaline earth metals are a group of six elements in the periodic table. They are beryllium (Be), magnesium (Mg), calcium (Ca), strontium (Sr), barium (Ba), and radium (Ra). The first five elements in this group have similar chemical properties, while radium is much less reactive.
All of the alkaline earth metals have low electronegativities. The most electronegative element in this group is beryllium, with an electronegativity of 1.57 on the Pauling scale. This is because beryllium has a small atomic radius and a high ionization energy.
The other five elements have electronegativities between 1.2 and 1.3. So, to answer the question, beryllium will have the greatest electronegativity among the alkaline earth metals.
Which Alkaline Earth Metal Has the Smallest Electronegativity?
The alkaline earth metal with the smallest electronegativity is beryllium. This is because beryllium has a smaller atomic radius than the other alkaline earth metals. The smaller the atomic radius, the fewer electrons there are in the outermost shell of an atom, and thus the less electron-electron repulsion there is. This results in a higher electronegativity for beryllium.
Which Alkaline Earth Metal Has the Highest Ionization Energy?
The alkaline earth metals are a group of elements in the periodic table with similar properties. They all have high ionization energies, meaning they require a lot of energy to lose an electron and become positively charged ions. The metal with the highest ionization energy is beryllium, followed by magnesium, calcium, strontium, barium, and radium.
Beryllium has an ionization energy of 938 kJ/mol, while magnesium has an ionization energy of 743 kJ/mol. Calcium, strontium, barium, and radium have ionization energies of 589 kJ/mol, 549 kJ/mol, 502 kJ/mol, and 419 kJ/mol respectively.
Conclusion
The alkaline earth metals are a group of elements in the periodic table. They include beryllium, magnesium, calcium, strontium, barium, and radium. The alkaline earth metals have high electronegativities. Beryllium has the highest electronegativity of any element in the periodic table.