Where Does All the Energy on Earth Come from
The sun is the source of all energy on Earth. Solar radiation drives our planet’s weather and climate and powers the photosynthesis that fuels plant growth. It also supports a vast array of other natural processes, from evaporation to ocean currents. And, of course, it warms us and makes life possible.
The sun is the source of all energy on Earth. It drives our weather, it warms our planet, and it powers the life that exists here. Solar radiation drives the water cycle and creates wind currents.
It also provides the energy that fuels plant growth and powers photosynthesis. All fossil fuels – oil, natural gas, coal – were formed from ancient plants and animals that were transformed by heat and pressure over millions of years. So, in a very real sense, we are all powered by the sun!
What Type of Energy Does the Earth Emit into the Atmosphere
The sun is the source of most of the energy that drives Earth’s climate and weather. It warms our planet from 93 million miles away. And though it may seem small in the sky, it’s huge—about 109 times wider than Earth.
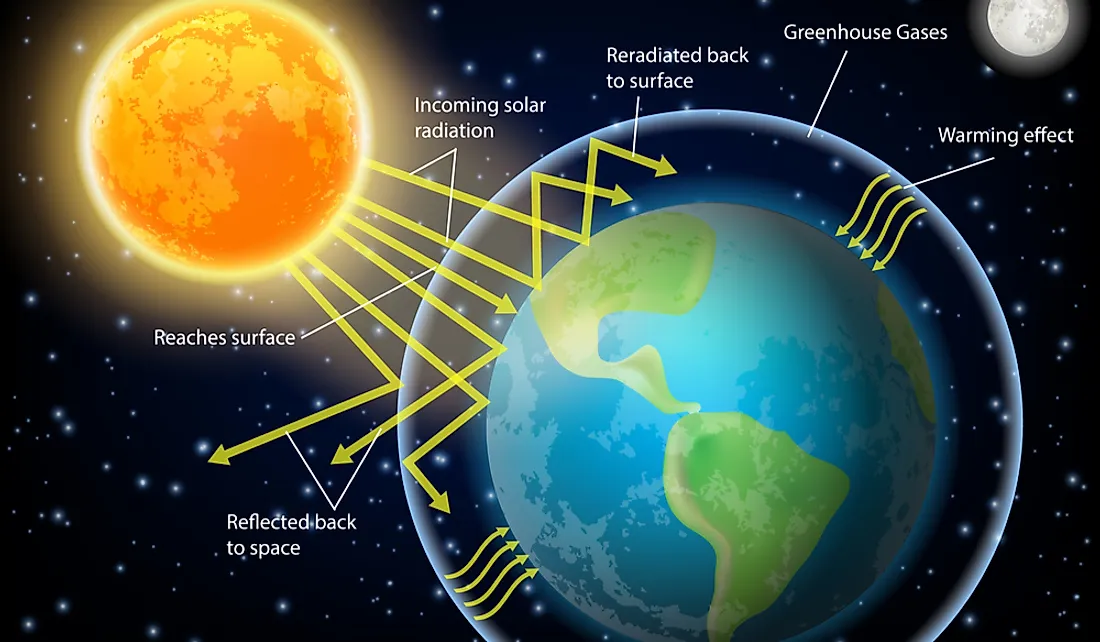
The sun is so bright that if all the light reflecting off Earth were focused into a single beam, it would be about as bright as a full moon on a clear night. But not all of the sun’s energy reaches us. Some are reflected back into space by clouds and particles in the atmosphere.
And some are absorbed by greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, like water vapor, carbon dioxide, and methane. These greenhouse gases trap heat in the atmosphere and make Earth warm enough to support life. Earth emits its own energy into space, too.
Our planet is constantly giving off heat—energy that it got from the sun billions of years ago when it formed. This heat escapes into space as infrared radiation. Greenhouse gases trap some of this heat close to the Earth’s surface, making our planet even warmer.

Credit: www.shsolarelectric.com
What is the Source of All the Energy on Earth
The sun is the ultimate source of all the energy on Earth. It drives the water cycle, which is responsible for the weather and climate. Solar radiation also powers photosynthesis which produces the food we eat and the oxygen we breathe.
How Does This Energy Affect Our Planet And Its Climate
The greenhouse effect is the process by which radiation from a planet’s atmosphere warms the surface of that planet. Greenhouse gases in the atmosphere trap energy from the sun. This trapped energy makes the Earth’s atmosphere warm and disturbs the Earth’s climate.
It happens because certain gases in the Earth’s atmosphere, like water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, and ozone, can trap heat. These “greenhouse gases” let sunlight pass through to the Earth’s surface, but they prevent some of the heat from escaping back into space. The more greenhouse gases there are in the atmosphere, the warmer it becomes on Earth.
Over time, human activities have released enormous amounts of greenhouse gases into Earth’s atmosphere. The primary human activity that emits greenhouse gases is burning fossil fuels such as coal and natural gas. Burning these materials releases carbon dioxide and other pollutants into the air.
Other human activities that contribute to greenhouse gas emissions include raising livestock (which emits methane), growing rice (which emits methane), deforestation (which removes trees that absorb carbon dioxide), and using certain types of refrigerants (which release hydrofluorocarbons).
All of these activities add more greenhouse gases to our already full atmospheric “budget”—and they cause our planet to warm even more than it would naturally without human interference. As temperatures rise, we see all sorts of impacts on our environment and society: melting glaciers; expanding deserts; stronger hurricanes; longer droughts; increased wildfires; declining crop yields; ocean acidification …the list goes on and on.
Climate change doesn’t just mean warmer weather—it means major disruptions to local ecosystems all around the world as well as large-scale societal changes like mass migrations away from coastal areas due to rising sea levels or dwindling food supplies resulting from extreme weather events or changed growing seasons.
And all of this has real consequences for human health, too: hotter temperatures lead to more heat-related illnesses like dehydration and heat stroke while changing precipitation patterns can exacerbate flooding or drought conditions, both of which can lead to disease outbreaks. Clearly, then, climate change isn’t just about pretty pictures of polar bears floating on melting ice caps—it’s a complex global problem with far-reaching implications for every single one of us.
So what can we do about it? To start with, we need to better understand how exactly climate change works —and what we can do to mitigate its effects both now and in future generations.
What are the Potential Consequences of Using This Energy Without Proper Care
There are many potential consequences of using this energy without proper care. One consequence is that you may not be able to control the energy and it could cause harm to yourself or others. Another consequence is that you could become addicted to the energy and it could lead to negative consequences in your life.
A guide to the energy of the Earth – Joshua M. Schneiderman
Conclusion
The sun is the ultimate source of all energy on Earth. Every other form of energy can be traced back to the sun, directly or indirectly. The sun’s energy arrives on Earth in two forms: sunlight and solar wind.
Some of this energy is converted into chemical energy by photosynthesis in plants, which forms the basis of the food chain. The rest is absorbed by the atmosphere and oceans, providing warmth and driving the global weather patterns that power the water cycle.