What Is An Enclave In Period 5 Ap World History
An enclave in Period 5 of AP World History (1750-1900) is a geographically distinct area that is politically or economically controlled by a foreign power. This can include a foreign military base, a diplomatic mission, a trading post, or a colony. Enclaves were a common way for empires to expand their influence and control over a region. During this period, European powers such as Britain, France, and Spain established and maintained enclaves in various parts of the world as a way to gain access to resources and markets. These enclaves often had a significant impact on the local population, leading to increased trade and cultural exchange, as well as to conflicts over land and resources.
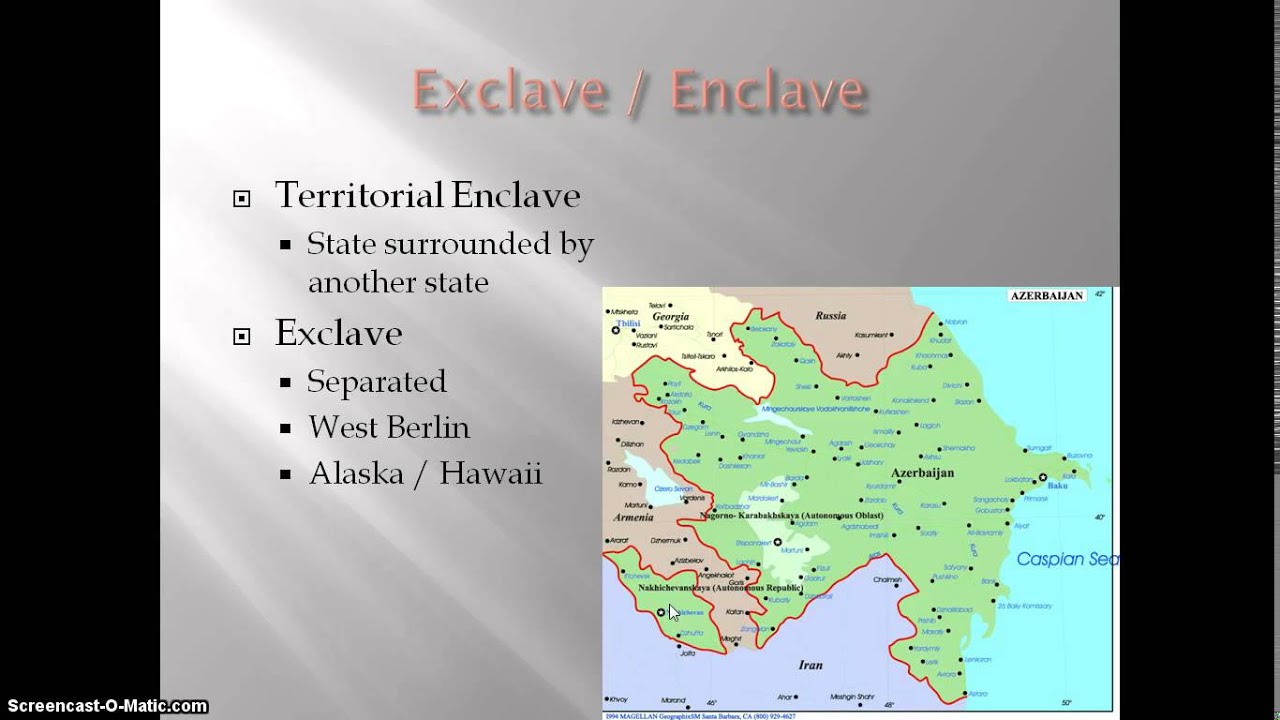
Definition of an Enclave
An enclave is a territory or region that is completely surrounded by a foreign land or nation. In the context of AP World History, an enclave is typically a small, independent nation that is completely surrounded by a larger, more powerful neighbor. These enclaves can be found in a variety of locations, including North America, Europe, and Asia.
Enclaves are important in period 5 (1750-1900) of AP World History because they provide a unique lens into the history of the period. During this period, Europe was becoming increasingly powerful and colonizing much of the world. This created a number of enclaves that were governed by their own laws and customs, and that often acted as a buffer between the powerful European nations and the rest of the world.
Enclaves were also important because they allowed for trade and other interactions between nations that may have otherwise been hostile. This type of commerce could be beneficial to both sides, as it allowed for increased economic growth and cultural exchange between nations.
In conclusion, an enclave is a small, independent nation that is completely surrounded by a larger, more powerful neighbor. In the context of AP World History, enclaves were important during period 5 (1750-1900) as they provided a unique lens into the history of the period, and allowed for trade and other interactions between nations that may have otherwise been hostile.
Historical Context of Enclaves
in Period 5
Enclaves are political entities that are completely surrounded by another, larger state. This geographical arrangement is not uncommon in history and has been a recurring theme in world politics for centuries. Period 5 of the AP World History course covers the period between 1750 and 1900 and enclaves played a major role in this era.
In particular, the 18th century saw the rise of the American and French Revolutions, which greatly affected the power dynamics of the world. This period also saw the formation of the British Empire, which was made up of a number of colonies around the world. These colonies were often surrounded by other states and were known as enclaves.
Enclaves had a wide range of effects on the politics and economics of the period. For example, the British Empire was able to exert economic control over its colonies due to its enclaves, while the French and Americans were able to gain strategic advantages due to their control over the enclaves.
Enclaves also played a role in the scramble for Africa, as European powers sought to control and exploit resources in the continent. In fact, the majority of African nations were created as a result of the European scramble for Africa, and many of these nations were enclosed by the European powers.
Overall, enclaves were an important part of the politics and economics of Period 5 and played a major role in shaping the modern world. They had a significant impact on the balance of power between states, the formation of colonies, and the scramble for Africa.
Types of Enclaves
In the fifth period of world history, an enclave is an area within which a country or other political entity is completely surrounded by a foreign power. Enclaves can be found in various parts of the world, from the United States and Mexico to India and Pakistan. This type of political entity is usually created by a treaty or agreement between two or more countries. There are three main types of enclaves: exclaves, condominiums, and protectorates.
Exclaves are small, independent states that are completely surrounded by another country’s territory, but remain politically distinct from the surrounding nation. They are often formed as a result of a peace treaty between two countries. An example of an exclave is the city of Kaliningrad, which is surrounded by the territory of Lithuania, but remains a part of the Russian Federation.
Condominiums are similar to exclaves, but are jointly governed by two or more countries. This type of enclave is usually formed when two countries are unable to agree on who should control a particular area. An example of a condominium is the Panama Canal Zone, which is jointly administered by Panama and the United States.
Finally, protectorates are areas of land that are under the control of a foreign power but remain politically distinct. Unlike exclaves and condominiums, protectorates are not completely surrounded by foreign territory. An example of a protectorate is the British Overseas Territories, which are under the control of the United Kingdom but remain politically independent.
These are the three main types of enclaves found in the fifth period of world history. Each type of enclave has its own unique characteristics and implications for international relations. Understanding these types of enclaves is essential for studying world history in this period.

Significance of Enclaves in Period 5
AP World History
In period 5 of AP World History, enclaves are significant because they provide a unique perspective into the past. Enclaves are a form of cultural and political boundaries that are formed by the interaction of different cultures and civilizations. They are regions that are isolated from the rest of the world, and are often surrounded by a larger, more powerful civilization. Enclaves can be seen in the form of the Mongol Empire, the Chinese Empire, the Ottoman Empire, and other empires throughout history.
Enclaves can provide valuable insight into the history of a certain region or culture. By looking at the enclaves, historians can gain insight into the different cultures and how they interacted with each other. They can also learn how certain civilizations or empires rose to power, and how they fell from it. Additionally, the enclaves provide historians with a unique look at the different religions and beliefs of the people living in those particular regions.
Enclaves can also be used to compare and contrast different cultures and civilizations during period 5 of AP World History. By looking at the different enclaves, one can see how different cultures interacted with one another, and how those interactions shaped their respective cultures. It can also provide information about the different social and political structures of the civilizations, which can help to explain why certain societies were more successful than others.
In conclusion, enclaves are important to consider when studying period 5 of AP World History. They provide historians with valuable insight into the different cultures and civilizations of the past, and how those cultures interacted with one another. By looking at the enclaves, historians can gain a better understanding of the different religions, beliefs, and social and political structures of the period.
Impact of Enclaves on World History
Enclaves, derived from the Latin “clavis” meaning “key”, are regions that are completely surrounded by another region. In world history, these distinct areas have had a powerful impact on the global landscape. As enclaves can be independent or part of a larger state, their influence can be seen throughout history in the form of trade, politics, and culture.
Enclaves have been used as sites for trade and commerce, as well as a refuge for persecuted minorities. In the Middle Ages, for example, Christian enclaves in the Middle East served as a safe haven for religious minorities. During the colonial era, enclaves such as the Portuguese fort of Diu in India provided a base for increased trade between Europe and Asia.
On the political front, enclaves have been used to assert a nation’s sovereignty over a region. For example, the Spanish enclave of Ceuta in North Africa is a remnant of Spain’s presence in the region. Similarly, the British enclaves of Hong Kong and Macau were used to support British interests in East Asia.
Finally, enclaves have had a significant cultural impact. Throughout history, enclaves have been used to preserve cultural heritage. In Latin America, there are numerous indigenous enclaves that retain their traditional cultures and languages. Similarly, in Central Asia, the enclaves of Wakhan and Badakhshan still boast vibrant cultural heritage.
In conclusion, enclaves have had a powerful impact on world history. From their use as sites for trade and refuge to their political and cultural influence, enclaves have helped shape the world as we know it. In Period 5 of AP World History, it is essential to understand the importance of enclaves to gain a deeper insight into the events of the past.
Challenges and Opportunities of Enclaves in Period 5
of AP World History
Enclaves are a unique type of territory which is surrounded by another country or state, yet still maintained political and cultural autonomy. Understanding the challenges and opportunities of enclaves in period 5 of AP World History can help to give insight into the global history of this period.
Enclaves have traditionally presented a unique set of challenges to their inhabitants. As a geographically isolated nation, enclaves often had to rely on trade and diplomacy with other nations to gain access to resources and to maintain their autonomy. Additionally, the lack of access to resources could lead to economic hardship for the people, as well as a lack of military strength.
On the other hand, enclaves also presented opportunities for their inhabitants. Being geographically isolated could help to protect the people from external threats, such as war or invasion. Additionally, enclaves could also serve as a hub for cultural exchange, allowing them to become more connected to the world without being affected by the politics of other nations.
Enclaves in period 5 of AP World History played an important role in the development of global history. From the rise of the Ming Dynasty in China to the establishment of the Dutch East India Company in Southeast Asia, the challenges and opportunities presented by enclaves in this period shaped the modern world. Understanding the history of enclaves in period 5 of AP World History can help to give insight into the global history of this period.
FAQs About the What Is An Enclave In Period 5 Ap World History
1. What is the purpose of an enclave in Period 5 of AP World History?
An enclave in Period 5 of AP World History is a region that is politically and/or culturally distinct from the surrounding areas. It can be an independent state, a protectorate, a nation within a nation, or a microstate, and its purpose is to provide a safe haven to a group of people who share a common identity.
2. What are the major examples of enclaves in Period 5 of AP World History?
Some of the major enclaves in Period 5 of AP World History include the Maronite Christians in Lebanon, the Coptic Christians in Egypt, the Baha’i in Iran, the Sikhs in India, and the Basques in Spain.
3. How does the concept of an enclave relate to other topics in AP World History?
The concept of an enclave is closely related to the topics of imperialism, nationalism, and globalization. Imperial powers often formed enclaves in order to control resources in foreign countries, while nationalist movements sought to establish enclaves in order to maintain their cultural and political autonomy. Globalization, meanwhile, has created new enclaves by allowing people to move across borders and create new cultural identities.
Conclusion
An enclave in Period 5 of AP World History is a distinct cultural, political, or economic entity surrounded by another country. Enclaves are often used as a way to protect a certain group or nation from outside interference or to create economic opportunities for the people living in the enclave. Enclaves have been used throughout history and have played an important role in the development of world history. By allowing distinct cultures and economies to exist within a larger country, enclaves have helped to create a more diverse and interesting world.