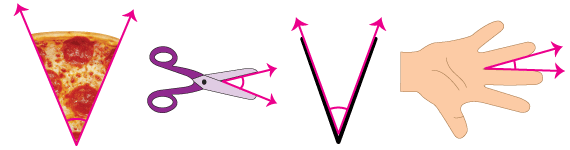
Real World Example Of An Angle
An angle is a geometric shape that is formed when two lines intersect each other. A real-world example of an angle can be found in any ordinary door. When the door is opened, the hinge forms an angle between the door and the frame. This angle is usually 90 degrees but can vary depending on the type of door. Other real-world examples of angles can be found in structures such as bridges, stairs, and even the corners of buildings.
Section 1: Definition of an Angle
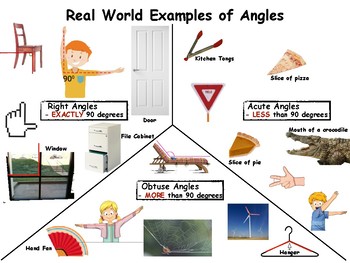
An angle is a figure formed by two rays, called the sides of the angle, sharing a common endpoint, called the vertex. An angle is measured in degrees, with a full rotation measuring 360°. Angles can be classified as acute, right, obtuse, and reflex, depending on the measure of the angle. Acute angles measure less than 90°, right angles measure 90°, obtuse angles measure between 90° and 180°, and reflex angles measure more than 180°.
In geometry, angles are an important concept that is used to describe the shape and size of objects. Angles can also be used to calculate the area of a triangle, the circumference of a circle, and more. Understanding the properties of angles and how they interact with other shapes helps students understand the basics of geometry.
In addition to the mathematical uses of angles, they are also used in everyday life. Angles can be seen in the construction of buildings, in furniture, and in many objects around us. Understanding angles and how they work can help us build better structures, make stronger furniture, and create useful objects.
Overall, angles are a fundamental concept in geometry and are used to measure the size and shape of objects. Angles can be used to calculate the area of a triangle, the circumference of a circle, and more. Understanding angles and how they interact with other shapes can help us build better structures, make stronger furniture, and create useful objects in everyday life.
Section 2: Different Types of Angles
Angle is a two dimensional shape in geometry that is formed when two lines intersect each other or meet at a point. There are many types of angles that are categorized based on measure, size, and shape. The most common types of angles include acute angles, right angles, obtuse angles, and straight angles. Acute angles measure less than 90 degrees and can be classified as acute, obtuse, or right angles. Right angles measure exactly 90 degrees and are the most common type of angle. Obtuse angles measure more than 90 degrees and are less common than right angles. Finally, straight angles measure 180 degrees and are the most uncommon type of angle.
When talking about angles, it is important to understand the basic principles of trigonometry. Trigonometry is the study of angles and their relationships to one another. Trigonometry is essential to understanding the different types of angles and how they interact with each other.
In addition to the different types of angles, there are also different ways to measure angles. One method of measuring angles is using a protractor. Protractors are used to measure angles by placing the protractor on the angle and then measuring the angle with the markings on the protractor. Another method of measuring angles is by using a ruler. This method involves placing the ruler on the angle and then measuring the angle with the ruler.
By understanding the different types of angles and how to measure them, one can gain a better understanding of angles in the real world. From construction, to engineering, to mathematics, angles play an important role in many aspects of everyday life.
Section 3: Properties of Angles
Angles have several properties that make them useful in a variety of contexts. For example, the angle’s measure is important in geometry and trigonometry. It can also be used to determine the direction of a line or the size of a triangle. Other properties of angles include the sum of the angles in a triangle, the exterior and interior angles of polygons, and the angle bisectors. Knowing these properties can help solve problems related to angles in the real world, such as determining the size of a roof for a house or the angle of a ramp for wheelchair accessibility. Additionally, angles can be used to measure the direction of a force or the movement of an object, giving engineers the ability to design structures that can withstand certain forces. For example, engineers must take into account the structural integrity of a bridge or building when calculating the angle of support beams and columns. Understanding the properties of angles and how they can be used in the real world is essential to mastering the mathematics behind angles.
Section 4: Constructing Angles with a Protractor
Constructing angles with a protractor is a common task for students in geometry classes. While the basics of using a protractor are fairly straightforward, understanding how to properly measure and draw angles can be tricky. To help students learn this concept, it is important to provide real-world examples of angles. By looking at examples found in everyday life, students can better understand how angles are formed and measured.
One of the most common real-world examples of angles is the roof of a house. Roofs are typically made up of several angles that are drawn to create a sloped surface. These angles can be measured using a protractor to determine the size and shape of the roof. Other real-world examples of angles can be found in architectural structures such as bridges and buildings. By measuring the angles of these structures, architects and engineers can ensure that the structure is structurally sound.
Real-world examples of angles are also found in nature, such as the angles formed by branches in trees. By measuring the angles of these branches, scientists can learn more about the growth and development of trees.
Students can also look for angles in everyday objects, such as the angles formed by the edges of a book or by the corners of a room. By measuring these angles, students can better understand angle measurement and gain a better understanding of how angles are used in everyday life.
Section 5: Examples of Angles in Everyday Life
Angles are all around us, and can be seen in many forms in our everyday lives. We use angles in architecture, engineering, and design, as well as in our everyday lives. From opening doors, to driving, to playing sports or even when cooking, angles are present everywhere.
In architecture, angles are used to support structures and create interesting shapes. Angles are used to create the shape of a building, and to shape the frames of windows and doors. Angles are also used to create interesting aesthetic designs.
In engineering, angles are used to create strong, stable structures. Angles are used to support bridges, towers, and many other structures.
In design, angles are used to create interesting and attractive shapes. From furniture to clothing to logos, angles are used to create interesting visual designs.
In our everyday lives, angles are used in many ways. We use angles to open and close doors, to drive a car, and to play sports. We also use angles when we cook, to make sure the food is evenly cooked.
We can also see angles in nature. From the shape of a tree to the angle of the sun, angles are everywhere in nature.
Angles are present in many forms in our everyday lives. From architecture and engineering to design and everyday activities, angles are a part of our lives. Learning about angles helps us better understand the world around us.
Section 6: Summary of an Angle’s Characteristics
Angles are an important mathematical concept that can be found in everyday life. They are used to measure the size of an object or the angle between two lines. Additionally, angles can be used to describe the relationship between two points, lines, or planes. An angle is uniquely characterized by its vertex, sides, and interior angles. It is also defined by its measure, which can be acute, right, obtuse, or reflex. Furthermore, angles can be classified as equal or unequal based on their measures.
The real-world application of angles is vast. From measuring the angles of a roof to determining the angle of a bridge’s span, angles can be used to help solve many problems. They also play a big role in navigation, allowing pilots to measure courses and distances between two points. Angles are even used in art to create perspective and to give the illusion of space.
In conclusion, angles are an important concept in mathematics with a wide range of applications in everyday life. By understanding the characteristics of an angle, one can better identify and use angles in a variety of situations.
FAQs About the Real World Example Of An Angle
1. What is a real world example of an angle?
A real world example of an angle can be found when two intersecting roads meet. Each road forms one side of the angle and the intersection of the roads forms the corner point of the angle.
2. Does a square or rectangle have angles?
Yes, a square or rectangle has four angles. The angles are formed by the four corners of the square or rectangle.
3. Are there any other real world examples of angles?
Yes, angles can also be found when two walls meet in a room, when two sides of a triangle meet, when two sides of a trapezoid meet, and when two sides of a pentagon meet.
Conclusion
An angle is a figure that is formed when two lines meet at a common point. In the real world, angles are found everywhere, from the sides of a triangle to the corners of a room. Angles are used in construction and design, and they are used to measure distances and directions. In summary, angles are an important part of everyday life, and they are found all around us.