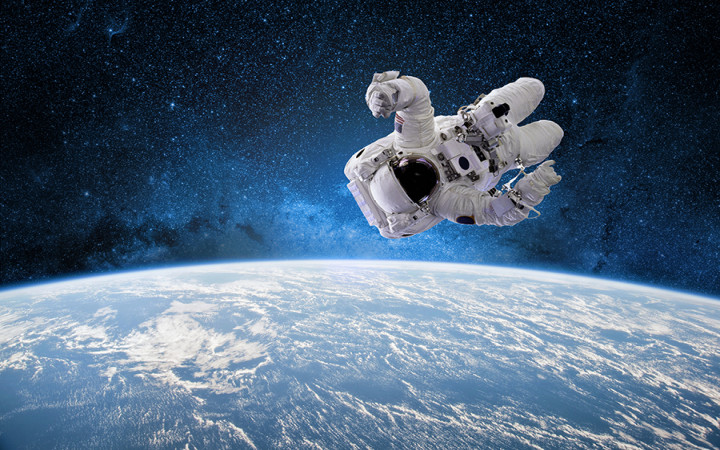
Is There A Zero Gravity In Space?
Zero gravity, or the sensation of weightlessness, is a physical experience that is often associated with space. While it is true that astronauts in space experience a type of zero gravity, it is not a feature of space itself. Rather, it is the result of a balance between the gravitational force of a large body, such as a planet or star, and the centrifugal force of the object orbiting that body. Astronauts in low Earth orbit experience a microgravity environment, where the force of gravity is much weaker than on the ground. This allows astronauts to float freely in their spacecraft, and creates the sensation of zero gravity.
What is Gravity?
Gravity is one of the fundamental forces of physics, and it plays an important role in the structure and stability of the universe. It is a force of attraction between two masses, and it is responsible for keeping everything in space from planets and stars to galaxies and clusters of galaxies together. But, is there a zero gravity in space?
The answer is both yes and no. While it is true that gravity is everywhere in space, it is not uniform in strength. On Earth, the gravity is strong enough to keep us from floating off into space, but in some parts of the universe, there are areas where gravity is so weak that it’s virtually undetectable. These areas are known as “zero gravity” or “micro-gravity” environments.
In space, the strength of gravity depends on the mass of the object. The more massive the object, the stronger the gravitational pull. For example, the gravity of a planet is much stronger than the gravity of an asteroid, and the gravity of a star is much stronger than the gravity of a gas cloud. In these zero gravity or micro-gravity environments, objects can move freely without being held in place by the force of gravity.
In short, while there is no truly zero gravity in space, there are certain regions that are close enough to zero that it can be considered a zero-gravity environment. It is within these environments that astronauts and researchers can experience and study the effects of weightlessness on objects and materials.
What is Zero Gravity?
Zero gravity is a term used to describe the state of weightlessness or a lack of gravitational pull experienced in outer space. It is a phenomenon that occurs when an object is in free fall and is pulled by gravity in all directions equally. This means that the object is no longer subject to the force of gravity and is instead floating in a state of perfect balance. This state of perfect balance is referred to as a ‘zero gravity’ environment. While zero gravity does exist in space, it is not a vacuum; it is still affected by the gravitational pull of nearby objects. For example, in the International Space Station, the astronauts experience a sensation of weightlessness due to the station’s orbit around Earth. This sensation is the closest thing to a zero gravity environment that can be experienced on Earth.
The Impact of Zero Gravity on Astronauts
Space exploration has been an ever-growing area of research with numerous opportunities for discovery and advancement. As a result, the exploration of space has opened up a new world of possibilities and insights, including the potential effects of zero gravity on astronauts. This article will explore the implications of zero gravity and provide an in-depth analysis of the impact on astronauts.
Zero gravity is the state of free fall, where there is no gravity acting on bodies. It is also known as microgravity, which is experienced in space. The concept of zero gravity has been explored for centuries, but in the modern day, space exploration has allowed us to discover its true effects on humans.
Astronauts in zero gravity are exposed to a variety of effects, both positive and negative. For example, during long-term missions in space, astronauts may suffer from bone and muscle loss, due to the lack of gravity. They also experience difficulty sleeping, as their body is not used to the sensation of free fall. Additionally, zero gravity can cause fluid shifts in the body, making astronauts feel nauseous and dizzy.
On the other hand, astronauts in zero gravity can also experience a variety of benefits. Studies have shown that astronauts often report improved moods and a sense of wellbeing while in space. Additionally, zero gravity has been found to improve hand-eye coordination, alertness, and reflexes. Astronauts also tend to experience a heightened sense of awareness and can often focus more easily.
Overall, the effects of zero gravity on astronauts vary depending on the individual and the duration of the mission. While there are some potential drawbacks, the overall benefits generally outweigh the risks. Thus, it is important to consider the impact of zero gravity on astronauts when planning and executing a space mission.
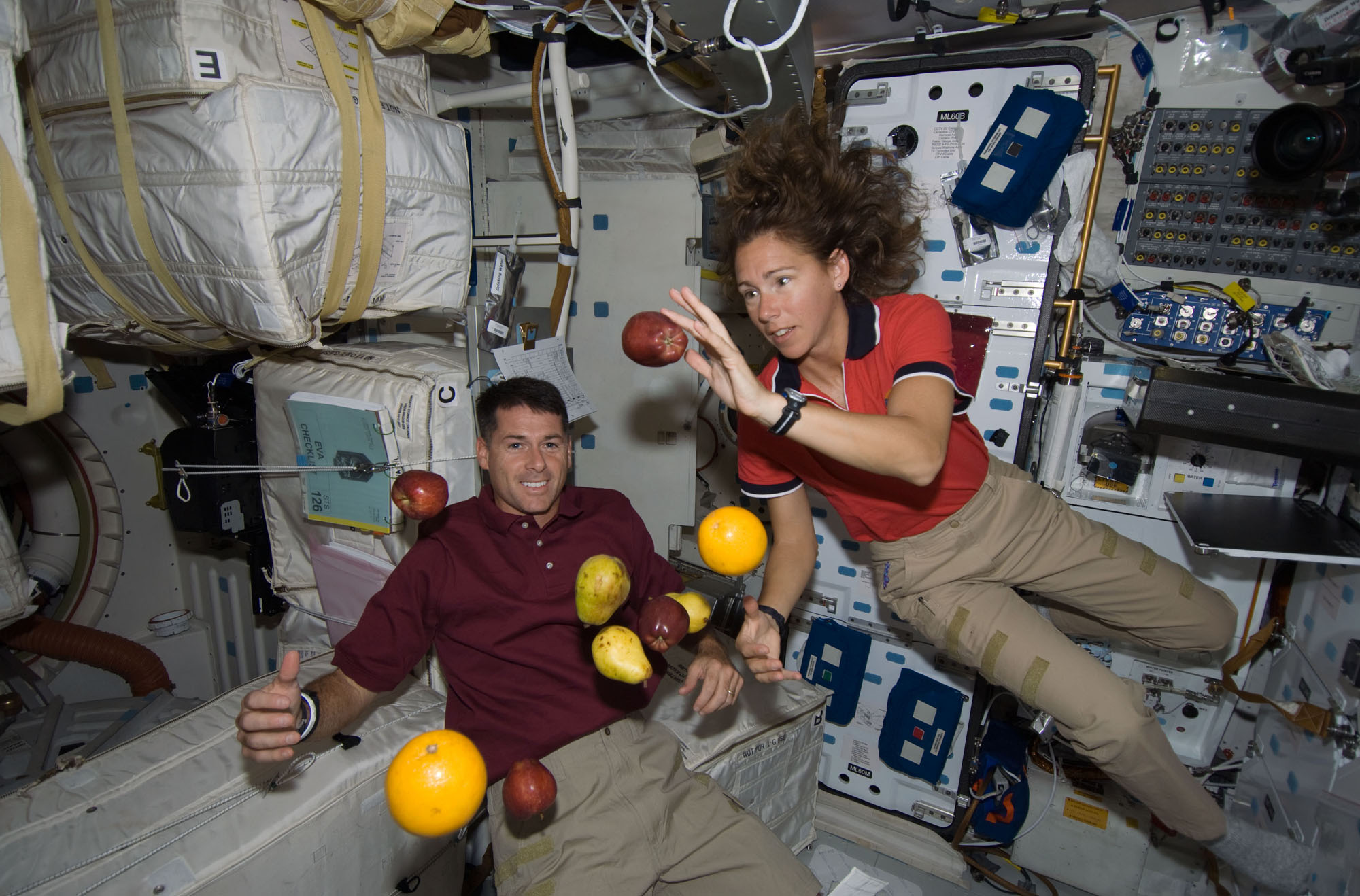

How Can Zero Gravity be Achieved in Space?
Space is the ultimate playground for scientists, adventurers, and space travelers alike. But what is zero gravity and how can it be achieved in space? Zero gravity, or microgravity, is the state of weightlessness experienced in space where the pull of gravity is reduced or eliminated. It can be achieved in several ways, including freefall, orbiting, and accelerating.
Freefall is probably the most well-known way of achieving zero gravity, and it occurs when a spacecraft or spacewalk is in a state of constant acceleration, allowing it to fall around the planet and experience the sensation of weightlessness. Orbits are another way to experience zero gravity, and astronauts can take advantage of the natural orbit of a planet or moon to float in a state of weightlessness.
Finally, accelerating is a process in which a spacecraft uses a combination of propulsion and gravity to move faster than the speed of light. This allows for a state of weightlessness, as the spacecraft is pulled inwards towards a planet or moon and away from Earth’s gravitational pull.
No matter which way you decide to experience zero gravity, it’s a unique and exciting opportunity to explore the wonders of the universe. From exploring the wonders of the International Space Station to performing experiments in microgravity, zero gravity can open up a world of possibilities. So, if you’re looking for a thrilling adventure, look no further than space.
Is There a Zero Gravity Area in Space?
Space is a mysterious and fascinating place that has been the subject of countless questions and discoveries, including the idea of zero gravity. Many people believe that zero gravity exists in space, but it’s far from the truth. In reality, gravity exists everywhere in the universe, including in space, but its effects are different. On Earth, gravity is the force that pulls objects towards the center of the Earth and keeps them in their orbits. In space, however, the same force exists, but it is much weaker, meaning that objects don’t experience the same pull as they do on Earth.
So, while there may not be a true “zero gravity” area in space, there are areas where gravity is weaker than on Earth. In these areas, objects can experience weightlessness and a sensation of floating in the air. This phenomenon is called microgravity and it is often experienced by astronauts during their space missions. In addition to this, scientists are researching ways to use microgravity to study how gravity affects various things, such as the behavior of molecules and the effects of space radiation on humans.
Ultimately, while zero gravity does not exist in space, there are areas where gravity is weaker than on Earth. Microgravity can provide us with valuable insights into the effects of gravity on the universe, and can be a great opportunity for exploration and research.
The Benefits and Challenges of Zero Gravity in Space
Space exploration has been an integral part of human history since the first successful satellite launch in 1957. In recent years, a key aspect of space exploration has been the concept of zero gravity. Zero gravity is defined as a condition in which the net force on an object is zero, and thus the object experiences no acceleration due to gravity. This has become an important part of space exploration, allowing astronauts to conduct research and experiments in a zero gravity environment.
The benefits of zero gravity in space are numerous. It allows astronauts to conduct experiments in a weightless environment, meaning that they can observe the effects of weightlessness on objects, organisms, and even themselves. In addition, astronauts can conduct experiments that would not be possible in Earth’s gravity, such as growing crystals in a weightless environment. Zero gravity also provides a unique perspective for astronauts to observe the universe, since they can observe the stars and planets in a way that is not hindered by the effects of gravity.
The challenges of zero gravity in space are also noteworthy. Astronauts must take special precautions to protect their health and safety in the zero gravity environment, as the lack of gravity can cause physical and psychological issues. In addition, conducting experiments in a zero gravity environment can be difficult and time-consuming, as objects can drift away and the lack of gravity can disrupt the accuracy of experiments.
Overall, zero gravity is an important part of space exploration, providing astronauts with the ability to conduct experiments and observe the universe in ways that would not be possible on Earth. While there are challenges to conducting experiments in a zero gravity environment, the benefits of zero gravity are numerous and well worth the effort.
FAQs About the Is There A Zero Gravity In Space?
Q: Is there zero gravity in space?
A: No, there is no zero gravity in space. While astronauts in space may appear to be floating, they are actually still subject to the gravitational pull of the Earth.
Q: Does microgravity exist in space?
A: Yes, microgravity does exist in space. This is the feeling of weightlessness experienced by astronauts in space, caused by the lack of gravity from external sources such as the Earth.
Q: Are there artificial gravity generators in space?
A: No, there are no artificial gravity generators in space. However, spacecraft have been designed to mimic the effects of gravity by spinning to create a centrifugal force.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the concept of zero gravity in space is an illusion. While there is no direct gravity in space, the objects within it are still subject to the law of gravitational attraction. Therefore, while there is no zero gravity, the feeling of weightlessness experienced in space is a result of the balance between gravity and a spacecraft’s inertia.