Is Milky Way Moving?
The Milky Way is our home galaxy, and like everything in the universe, it is constantly in motion. This motion is complex and hard to measure, but astronomers have studied it closely and determined that the Milky Way is moving at a speed of approximately 600 km per second relative to the cosmic microwave background radiation. This motion is believed to be caused by the gravitational pull of other galaxies, such as Andromeda, which is located about 2.5 million light years away from us. The Milky Way is also spinning, which causes stars on its outer edges to move faster than those closer to the center. Over time, this motion will cause the shape of the Milky Way to change, and its stars to move around.
What is the Milky Way?
The Milky Way is the galaxy in which our Solar System resides. It is a vast collection of gas, dust, and billions of stars, including our own Sun. This immense spiral galaxy, which is roughly 100,000 light-years across, is home to more than 100 billion stars. It is believed that the Milky Way is constantly moving, with its stars and other objects rotating around its core. Scientists have been studying the movement of the Milky Way for centuries, and new technology has allowed them to gain a deeper understanding of the galaxy’s motion. In this blog post, we’ll explore the Milky Way’s motion and how it affects our lives. We’ll also take a look at some of the most recent research on the topic and what it means for the future.
The Milky Way’s Motion in Space
The Milky Way is our home galaxy, and while we may think of it as static and permanent, it is actually moving in space. Scientists estimate that our galaxy is moving at a speed of about 550 km/s relative to the cosmic microwave background radiation. This means that the Milky Way is actually moving through space at a rate of two million miles per hour!
The reason for this motion is due to the gravitational pull of the mass concentrations in the universe. As the Milky Way, along with other galaxies, orbits the supermassive black holes in the centers of galaxies, it is pulled along by the gravity of these large objects. This causes the Milky Way to move in an elliptical pattern around the black hole, and its velocity is determined by the amount of mass in its surrounding environment.
The Milky Way’s motion is also affected by the expansion of the universe, which causes the galaxies to move away from each other. This phenomenon is known as the Hubble Flow, and it is responsible for the Milky Way’s gradual movement through space.
As the Milky Way moves, it also interacts with other galaxies in the universe, creating gravitational waves that affect the shape and structure of our galaxy. Over time, these interactions can cause the Milky Way to rotate faster or slower, and even change its orientation in space.
The Milky Way’s motion in space is an exciting prospect for astronomers and astrophysicists alike. By studying the motion of our galaxy, we can gain valuable insights into the structure and evolution of the universe. As we continue to explore the Milky Way’s motion, we will be able to better understand the cosmos and our place within it.
Discoveries of the Milky Way’s Motion
The Milky Way galaxy is an ever-evolving celestial body, and recent discoveries have revealed that it is in constant motion. Astronomers have long studied the Milky Way’s motion and have determined that it is moving through the universe at an astonishing speed of around 552 kilometers per second. This motion is referred to as radial velocity, as the Milky Way is currently moving away from the center of the universe.
Using high-powered telescopes and other advanced instruments, astronomers have been able to observe the movement of the Milky Way and other galaxies in the universe. These observations have shown that the Milky Way is moving in an elliptical orbit, which is similar to a racetrack. This motion is driven by the force of gravity from other galaxies and objects in the universe, causing the Milky Way to move in an ever-changing path.
The rate of the Milky Way’s motion is determined by its mass and the combined gravitational pull of other objects in the universe. As it travels through space, the Milky Way is constantly being affected by the gravitational forces of the galaxies and objects it encounters, which can result in changes in its speed and direction.
The Milky Way’s motion is an important part of understanding the universe, as it helps astronomers better understand the formation and evolution of galaxies. By studying the motion of the Milky Way, scientists can gain insight into how galaxies interact with each other, and how their motion affects the universe.
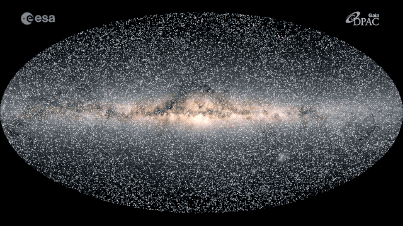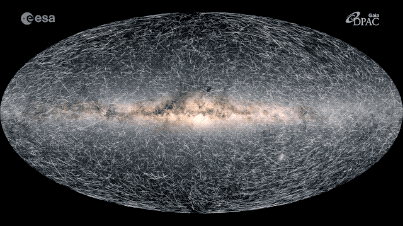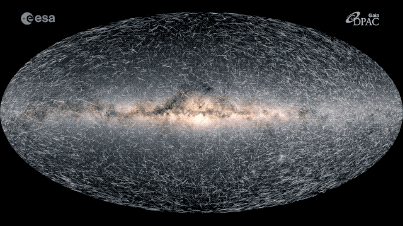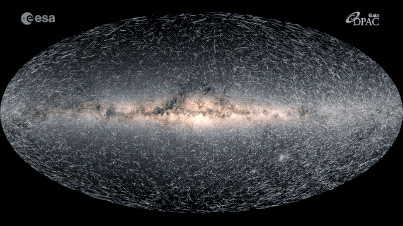
The Milky Way’s Impact on Astronomy
Deep within the unknown depths of the universe, the Milky Way has been a source of fascination for many centuries. Throughout its history, the Milky Way has had a tremendous impact on the study of astronomy. Scientists have studied the galaxy to learn more about its structure, composition, and origin, in addition to the many stars and galaxies that make up the Milky Way. In addition to providing a wealth of knowledge about the universe, the Milky Way has also helped to shape our understanding of the laws of physics and the formation of galaxies.
The Milky Way’s structure is composed of a spiral arm, a central bar, and a bulge. The spiral arm is the most visible feature of the galaxy, as it contains bright stars and many galaxies. The central bar is the densest region of the Milky Way, containing a large amount of dark matter. The bulge is a dense region of stars around the center of the galaxy. This region also contains a supermassive black hole.
The Milky Way’s composition is composed of gas, dust, and stars. The gas and dust make up most of the galaxy’s mass and provide the material for star formation. The stars, on the other hand, are the main source of light and heat. The Milky Way also contains a variety of elements, including hydrogen, helium, and a variety of metals.
The origin of the Milky Way is still a mystery. Astronomers believe that the galaxy was formed from the collision of two smaller galaxies, but the exact process is still unknown. The Milky Way has also been studied to better understand the process of galaxy formation and the laws of physics.
The impact of the Milky Way on astronomy is undeniable. By studying the galaxy, astronomers have gained valuable insights into the structure, composition, and origin of the universe. The Milky Way has also helped to shape our understanding of the laws of physics and the formation of galaxies.
Recent Developments in Milky Way Motion Research
Humans have long been fascinated by the night sky, both for its beauty and its mystery. For years, astronomers have studied the Milky Way and its various star systems, noting the movements of these stellar bodies. Now, thanks to recent advances in technology, scientists have been able to make more precise observations of the Milky Way’s motion.
Recent research has shown that the Milky Way is moving at a speed of about 600,000 miles per hour. This is faster than the speed of light, making it one of the fastest-moving objects in the universe. Although this motion is relatively small compared to the vastness of the Milky Way, it is still significant. Scientists believe that this speed is due to the gravitational pull of neighboring galaxies, such as the Andromeda Galaxy.
In addition, recent research has revealed that the Milky Way is not only moving in one direction, but in multiple directions. It is moving in a spiral-like pattern, and its motion is affected by the gravity of other nearby galaxies. This complex motion could help scientists better understand the structure of the universe, and how it evolves over time.
The recent developments in Milky Way motion research are providing us with valuable insights into the structure and evolution of the universe. By studying the motion of the Milky Way, astronomers are able to better understand the laws of physics and how they govern the universe. This knowledge is helping us uncover the mysteries of the cosmos and gain a greater appreciation for the beauty of the night sky.
Conclusions: Is the Milky Way Moving?
The Milky Way is a complex and constantly evolving system, so it is difficult to definitively answer whether it is moving. Astronomers have used various observational methods to measure its motion, such as tracking other galaxies to measure our speed relative to them. The results of these studies suggest that the Milky Way is indeed moving, with a velocity of around 552 km/s relative to the rest of the universe. However, the actual motion of the Milky Way is much more complicated, as it is affected by many different processes, such as the gravitational pull of other galaxies and the expansion of the universe. Ultimately, the exact speed and direction of the Milky Way can only be determined by further research and observation.
FAQs About the Is Milky Way Moving?
Q: Is the Milky Way galaxy moving?
A: Yes, the Milky Way galaxy is moving at a speed of approximately 552 km/s relative to the Cosmic Microwave Background.
Q: How fast is the Milky Way moving?
A: The Milky Way is moving at a speed of approximately 552 km/s relative to the Cosmic Microwave Background.
Q: What direction is the Milky Way moving?
A: The Milky Way is moving in the direction of the constellation Hydra, which is located in the southern sky.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Milky Way is in fact moving. It is moving at a speed of approximately 552 kilometers per second with respect to our local group of galaxies, and is moving towards the constellation Virgo. Our solar system is also moving in the same direction. Although this movement is slow, it is only part of the larger motion that our galaxy makes as it orbits the center of the universe.


