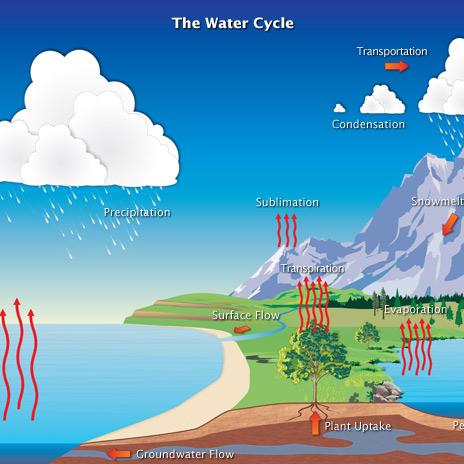
How the Earth Works
The Earth is a fascinating place. It’s huge and old and full of mystery. How does it work?
How did it come to be? Scientists have been trying to figure that out for centuries, and they’ve made some pretty amazing discoveries. Here are just a few of the things we know about how the Earth works.
The Earth is a pretty amazing place. It’s huge and old and full of all kinds of interesting things. But how does it work?
The Earth is actually a giant rock. It’s made up of lots of different materials, like iron and magnesium and silicon. These materials are all put together in a really big way, making the Earth about 4.5 billion years old.
The Earth has lots of different layers. The outermost layer is called the crust. This is where we live!
The next layer down is called the mantle. This is made up of hot rocks that flow around under the crust. The innermost layer is the core, which is made up of even hotter rocks and metals.
All these layers are held together by gravity, which keeps everything in its place. Gravity also makes sure that the Earth spins around on its axis once every day, giving us day and night. And gravity pulls us towards the center of the Earth, so we don’t float off into space!
How the Earth Works Discovery Channel
Volcanoes are one of the most awe-inspiring geological features on Earth. These giant mountains, formed by the release of molten rock and ash from deep within the planet, have shaped our planet’s surface over millions of years. Today, there are around 1,500 active volcanoes on Earth – and many more that are inactive or dormant.
Volcanic activity can be found all over the world, from Iceland to Hawaii. While volcanoes can cause devastating natural disasters, they also play an important role in shaping our planet and making it habitable for life. Volcanoes are responsible for creating some of the world’s most stunning landscapes and providing vital nutrients for plants and animals.
If you’re fascinated by volcanoes and want to learn more about how they work, Discovery Channel’s How the Earth Works is a great place to start. This three-part series explores everything from the history of volcanic eruptions to the science behind these incredible natural phenomena.

Credit: www.goodreads.com
How Does the Earth Work?
The Earth is a big, round rock that revolves around the sun. It’s pretty simple, really. The sun is a star and it’s huge and hot and has a lot of energy.
The Earth is much smaller than the sun, and it’s not nearly as hot. But the Earth does have some energy of its own. The Earth gets its energy from two main sources: the sun and radioactive elements deep inside the planet.
The sun provides most of the Earth’s energy in the form of sunlight. This sunlight powers plants, which convert it into food for animals to eat. Animals then use this food to power their bodies and do all sorts of things, like running and jumping and playing fetch with sticks (well, maybe not that last one).
Radioactive elements deep inside the planet provide a small but steady stream of energy that helps keep the planet warm enough for life to exist on it. Without this heat from within, the surface of our planet would be a frozen wasteland! So we have these two sources of heat – from the sun and from inside the Earth – that make our planet just right for life as we know it.
How Did Earth Form Step by Step?
It is thought that the Earth was formed about 4.6 billion years ago. The first step in its formation was the accretion of gas and dust in the protoplanetary disk around the young Sun. Over time, this material began to clump together and form larger and larger bodies.
Eventually, there were a few large bodies, or planetesimals, left in the disk. As these bodies continued to grow through collisions, they began to heat up due to gravitational compression. This caused them to release their gravity-held gas and dust, which resulted in a giant impact event between two large planetesimals.
This impact created our Moon and blasted debris into orbit around Earth. The final steps in Earth’s formation were the accretion of small planetesimals and the differentiation of our planet’s interior by density.
How Did Earth Become Earth?
The prevailing scientific theory is that the solar system, including Earth, was formed from a huge cloud of gas and dust called the solar nebula. This nebula was composed of hydrogen and helium, with trace amounts of other elements. Over time, the gravity of the central mass caused the cloud to collapse in on itself.
As it did so, it began to spin faster and flatten out into a disk shape. As the disk continued to collapse, it grew hotter in the center due to gravitational compression. This eventually led to nuclear fusion reactions taking place, creating our Sun.
The Sun’s heat and light then caused the outer parts of the disk to expand and dissipate. What remained after this process was a flattened disk of material orbiting around the young Sun. This material gradually coalesced into planets through a combination of accretion (gravitational attraction between particles) and collisions.
Earth is thought to have formed in this way over 4.5 billion years ago.
How the Earth works (as seen from space) – All parts
Conclusion
The Earth is huge and full of many different processes. From the way it was formed, to the way it changes over time, there is a lot to learn about how the Earth works. This blog post covers some of the basics of the Earth’s history and geology.
It also explains how plate tectonics, volcanoes, and earthquakes work.