How Much of the Earth is Desert
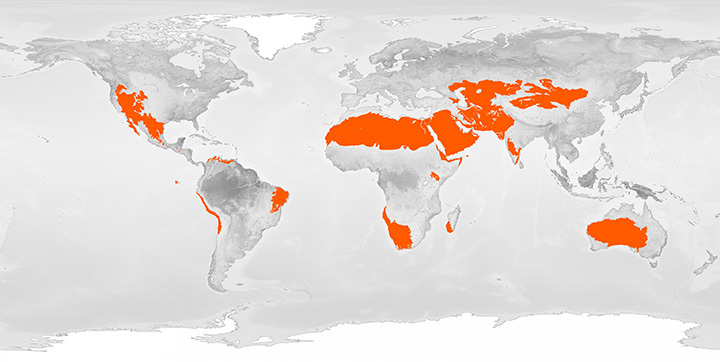
A desert is a landscape or region that receives very little precipitation. Deserts can be found throughout the world, especially in Africa, Australia, and South America. They are also common in the United States, where they cover about one-third of the land area. The largest desert in the world is Antarctica.
Did you know that about one-third of the Earth’s surface is desert? That’s a lot of sand! The Sahara Desert alone is about the size of the United States.
But not all deserts are hot and sandy. Some, like the Gobi in Asia, are cold and rocky. And others, like the Mojave in North America, are dry and dusty.
So why is there so much desert on our planet? It turns out that deserts form when an area gets more sunlight than rainfall. This can happen when a region is far from any large bodies of water (like an ocean), or when it has a climate that doesn’t support much rainfall.
Interestingly, human activities can also create deserts. For example, when people overgraze an area by letting their animals eat too much of the vegetation, it can turn into a desert. And when farmers clear large areas of land for farming, they can also create conditions that lead to desertification.
Fortunately, there are things we can do to help prevent deserts from forming. We can manage our grazing animals better, and be careful not to over-farm our land. We can also plant trees and other plants that help hold moisture in the soil and prevent erosion. By taking these steps, we can help keep our planet green and habitable for generations to come!
What is the Largest Desert in the World
There are many deserts on Earth, and they come in all shapes and sizes. The largest desert is the Sahara Desert, which covers a vast area of northern Africa. This arid region gets very little rainfall and is home to a variety of different animals and plants that have adapted to harsh conditions.
Despite its dryness, the Sahara is actually teeming with life, and it is one of the most fascinating places on our planet.

Credit: www.dkfindout.com
What Percentage of the Earth’s Surface is Desert
According to National Geographic, approximately one-third of the Earth’s surface is desert. This means that about one billion people live in drylands, which include not just deserts but also dry grasslands, savannas, and shrublands. The Sahara Desert alone covers 3.6 million square miles (9.4 million square kilometers) and extends across 11 countries in North Africa: Algeria, Chad, Egypt, Eritrea, Libya, Mali, Mauritania, Niger, Sudan, Tunisia, and Western Sahara.
What are the Largest Deserts on Earth
There are many large deserts on Earth. The largest desert is the Sahara Desert, which covers 9.2 million square kilometers in Africa. The second largest desert is the Arabian Desert, which covers 2.6 million square kilometers in Asia and Northern Africa.
Other large deserts include the Gobi Desert (1.3 million square kilometers), the Kalahari Desert (900,000 square kilometers), and the Taklamakan Desert (330,000 square kilometers).
Why are There Deserts on Earth
Deserts are areas where evaporation exceeds precipitation. They occur under a variety of climatic conditions, but all deserts share certain features: They are dry (receive very little rainfall), have high daytime temperatures, and have a large diurnal temperature range (the difference between the day and night temperatures). Deserts generally form in two ways.
The first is when an area experiences a prolonged period of drought. Over time, as the lack of water causes plants to die and soils to erode, the landscape changes and becomes increasingly desert-like. The second way that deserts can form is through what’s called “orographic lift.”
This occurs when air flows up over mountains, cools down, and precipitates out its moisture onto the windward side of the mountain range. The leeward side of the mountains then experiences much drier conditions. There are four main types of deserts on Earth: hot and dry deserts, semi-arid deserts, coastal deserts, and cold deserts.
Hot and dry desert climates are found in subtropical regions around 30 degrees latitude North and South of the equator. These include places like the Sahara Desert in Africa, the Arabian Desert in Southwest Asia, and parts of Australia’s Great Victoria Desert. Semi-arid desert climates are drier than steppe climates but not as dry as true deserts; they usually receive between 10 and 20 inches (250 to 500 millimeters) of rain per year.
Coastal deserts are found along cold ocean currents; they tend to be foggy or cloudy much of the time due to the moist air being cooled by these currents. Cold desert climates are found at high altitudes or latitudes further from the tropics than hot/dry desert climates; they can also form near cold ocean currents like coastal deserts but don’t necessarily need to be located near them.
How Do Plants And Animals Adapt to Life in the Desert
Deserts are one of the most extreme environments on Earth. Plants and animals have to adapt to survive in these hot, dry conditions. One way that plants adapt to life in the desert is by storing water.
Many desert plants have thick, fleshy leaves that act like sponges and can hold a lot of water. Other desert plants have long, deep roots that help them reach underground water sources. Animals also have to adapt to survive in the desert.
Some animals, like lizards and snakes, have adapted to live without much water by becoming what scientists call “ectotherms” – animals that rely on external sources of heat to regulate their body temperature. These animals bask in the sun to warm up their bodies and become very active during the cooler nighttime hours when it’s harder for them to find food and water. Other animals, like camels and kangaroo rats, have developed special adaptations for dealing with water shortages.
Camels store fat in their humps which they can use for energy when there is no food or water available. Kangaroo rats get all the moisture they need from the seeds they eat – they never need to drink water!
What Impact Does Desertification Have on People And the Environment
Desertification is a form of land degradation in which a dryland ecosystem becomes increasingly arid, typically losing its vegetation and wildlife. The process of desertification is caused by a variety of factors, including climate change, overgrazing, poor irrigation practices, and deforestation. When these factors combine, they can create conditions that are conducive to desertification.
The impact of desertification on people and the environment can be significant. Desertification can lead to decreased crop yields and grazing land productivity, which can adversely affect food security. In addition, it can cause loss of habitat for plants and animals, as well as increased soil erosion and dust storms.
All of these impacts can have serious consequences for human health, economic development, and the overall well-being of affected communities. While the effects of desertification are often negative, there are some potential positives that could come from this process. For example, in areas where rainfall is scarce, the loss of vegetation cover could actually lead to an increase in water availability for humans and other animals.
In addition, desertified landscapes can provide opportunities for carbon sequestration and other forms of environmental mitigation. Ultimately, though, the negative effects of desertification far outweigh any potential benefits.
How 33% Of Earth’s Land Surface Is Covered By Deserts. Test Your Knowledge On World’s Desert Today.
Conclusion
The Sahara desert is the largest hot desert in the world, and it covers about 3.6 million square miles. That’s about the size of the United States! But deserts aren’t just dry, sandy places. They can be cold too. The Gobi desert in Asia is a cold desert. It gets very little rain and snowfall each year.
So, how much of the Earth’s surface is covered by desert? It turns out that about one-third of the Earth’s land surface is classified as desert. That means that deserts cover about 24 million square miles of our planet.