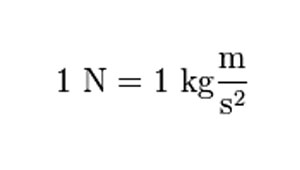How Much Is 1 N * M?
1 N * M is a mathematical expression used to represent the product of two numbers, N and M. It is typically used in algebra, geometry, and calculus to help solve equations and problems. The value of 1 N * M is determined by multiplying the two numbers together. For example, if N is 5 and M is 10, then the answer is 50. The result of 1 N * M can also be used to represent an area or a volume depending on the context in which it is used.
Defining N and M
can be a challenge at times. N and M are two mathematical variables that are often used in equations and calculations. N is a numerical value that can represent any number, positive or negative, while M is a numerical value with a specific range of values.
The value of N * M depends on the values of N and M. For example, if N and M are both equal to 4, then the value of N * M is 16. On the other hand, if N is 8 and M is 2, then the value of N * M is 16. This is because multiplying two numbers, no matter what their value is, always results in the same product.
The value of N * M can also be determined by using the distributive law of multiplication. This law states that multiplying a number by the sum of two numbers is the same as multiplying the number by each of the two numbers individually. So, for example, if N is 6 and M is 4, then the value of N * M is 24. This is because 6 * (4 + 4) is the same as 6 * 4 + 6 * 4, which is 24.
To sum up, the value of N * M is determined by the values of N and M. It can be calculated by multiplying the two numbers, or by using the distributive law of multiplication. No matter what the values of N and M are, the value of N * M will always be the same.
Elements of an N * M Calculation
Calculating N * M can be a tricky task, especially if you’re dealing with large numbers. Fortunately, there are a few simple steps you can take to make the process easier. First, N and M must be defined. N is the number of rows and M is the number of columns. Next, each element of the matrix (or matrix element) must be calculated. The element is the product of the corresponding row and column numbers. For example, if N = 3 and M = 2, the element (3,2) would be 6. Finally, the total of all the elements is the product of N * M. In this example, 3 * 2 = 6, which is the total of all elements. To summarize, N * M is the product of the number of rows and columns in a matrix, and each element of the matrix is the product of the corresponding row and column numbers.
Benefits of Understanding N * M Calculations
N * M is an important calculation used in many different fields, from engineering and finance to mathematics and physics. It’s important to understand the concept of N * M in order to make informed decisions and get the most out of your projects. While the calculation itself can seem complex, it’s easy to grasp once you understand the basics. N * M calculations can help you quickly and accurately calculate the size of certain objects or materials, the force of a reaction, and the number of items needed for a project.
By understanding N * M calculations, you can easily determine the amount of material needed for a project, the total cost of materials, and the total cost of labor. You can also use N * M calculations to measure the force of any reaction, and to determine the size of objects and materials. Knowing the value of N * M can help you make more informed decisions and be more efficient with your projects.
In addition, understanding N * M calculations can help you save time and money. With the help of N * M calculations, you can easily calculate the number of items needed for a project or the cost of materials and labor, allowing you to make more informed decisions and optimize your budget. Furthermore, it can help you make more accurate predictions and develop better strategies for your projects.
Overall, understanding N * M calculations can help you save time and money, make better decisions, and optimize your budget. With the help of N * M calculations, you can make more accurate predictions and develop better strategies for your projects.

How N * M Calculations are Used in Business
The calculation of N * M is a fundamental concept in business, used to measure the level of production and efficiency. It is a measure of the number of items produced or services rendered in relation to the number of resources used. N * M calculations are essential in determining the return on investment (ROI) of a business. This calculation is used to measure the efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and productivity of a business.
Calculating N * M is a basic tool used to measure the effectiveness of a business. Companies often use N * M to assess the profitability of different activities and processes. By comparing the cost of producing a product or service to the number of items produced or services rendered, businesses can gauge the efficiency of their operations. N * M calculations can also be used to determine the cost of producing a certain number of items or services relative to the resources used.
N * M calculations are also important in predicting future performance. By analyzing the data from previous N * M calculations, businesses can project future levels of production and efficiency. This allows companies to plan accordingly and make informed decisions about their operations.
In conclusion, N * M calculations are an essential tool used by businesses to measure the efficiency and productivity of their operations. By analyzing the data from previous calculations, businesses can predict future performance and make informed decisions about their operations. N * M calculations are an invaluable tool for businesses to make sure they are getting the maximum return on their investments.
Different Types of N * M Calculations
N * M calculations are one of the most common mathematical operations used in many areas of life, whether it be science, business or finance. There are a variety of different N * M calculations that can be used to give an answer to a particular problem or to calculate the amount of something. Knowing the different types of N * M calculations can be very useful in order to get the correct answer for whatever it is you are trying to calculate.
The most basic type of N * M calculation is the multiplication of two numbers. This type of calculation is used to find the product of two numbers and is often referred to as the ‘times’ calculation. Multiplication is used in many areas, including finance and economics, as it allows for the calculation of interest rates and other financial calculations.
Division is another type of N * M calculation. This type of calculation is used to find the quotient of two numbers. Division is often used in mathematics and science, and it can also be used to calculate the amount of something from two different numbers.
Addition and subtraction are also two types of N * M calculations. Addition is used to add two or more numbers together, while subtraction is used to take away one number from another. Both of these calculations are often used in mathematics and science, and they can be used to calculate the amount of something from two or more different numbers.
Finally, exponents are also a type of N * M calculation. Exponents are used to calculate the power of a number. This type of calculation is often used in mathematics and science, and it can be used to calculate the amount of something from two or more different numbers.
Therefore, it is important to understand the different types of N * M calculations and how they can be used to get the correct answer for whatever it is you are trying to calculate. Knowing how to use these different types of calculations can be very helpful in a variety of situations.
Common Examples of N * M Calculations
N * M, or N multiplied by M, is an expression used to calculate the value of a quantity when both the number of items and the value of each item are known. This calculation is useful when trying to determine the overall cost of a product or service. The answer can be found by multiplying the two numbers together. To better understand how to calculate N * M, let’s look at some common examples.
For example, a customer purchases six apples at $2 each. The total cost of the apples can be found by multiplying 6 (N) by $2 (M), yielding a total cost of $12. In another example, a clothing store holds a sale where all items are 25% off. The original cost of a shirt is $20, so to calculate the discounted price, one would multiply 0.25 (N) by $20 (M), finding the discounted price to be $5.
The N * M calculation is also useful in determining the area of a room. For example, if a room is 8 feet wide (N) and 10 feet long (M), the area of the room can be found by multiplying 8 by 10, yielding an area of 80 square feet.
In conclusion, N * M calculations are a useful way to determine the cost, price, or area of a quantity when both the number of items and the value of each item are known. By multiplying the two numbers together, one can find the total cost, discounted price, or area of a given item or space.
FAQs About the How Much Is 1 N * M?
1. What is N and M in the question “How Much Is 1 N * M”?
Answer: N and M are variables that represent two numbers that are multiplied together.
2. How can I calculate the answer to “How Much Is 1 N * M”?
Answer: To calculate the answer to “How Much Is 1 N * M”, multiply the two numbers represented by N and M together.
3. Is there a specific answer to the question “How Much Is 1 N * M”?
Answer: The answer to the question “How Much Is 1 N * M” depends on the numbers represented by N and M, so there is not a specific answer.
Conclusion
The answer to the question “How Much Is 1 N * M?” depends on the two numbers in question, N and M. If N and M are both whole numbers, then the product of N and M is the answer. If either N or M is a fraction or decimal, then the product of N and M will also be a fraction or decimal.