How Long Did The Earth Freeze?
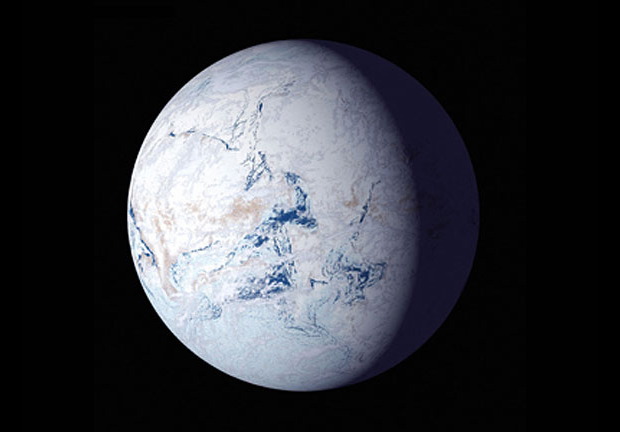
The Earth’s climate has changed dramatically throughout its history. One of the most extreme periods of cooling occurred during the Huronian glaciation, which is estimated to have taken place around 2.4 – 2.1 billion years ago. This glaciation was so extreme that it is believed to have caused a global freeze, with much of the Earth’s surface becoming encased in ice. Scientists estimate that the Huronian glaciation lasted for around 200 million years, give or take 50 million years. This was one of the longest ice ages in Earth’s history and is believed to have had an immense impact on the development of life on the planet.
Causes of the Earth’s Freeze
The Earth is a dynamic planet and its climate can change drastically over time. Recently, scientists have been studying the causes of an ongoing global freeze that has been occurring for centuries. The most widely accepted theory is that the Earth’s freeze is caused by the decrease in solar activity, which causes the Earth to not receive as much sunlight. This, in turn, causes the planet to cool down and the snow and ice to accumulate. It is also possible that a decrease in volcanic activity and an increase in aerosols in the atmosphere could be contributing factors. Finally, the orbital variations of the Earth have also been studied as potential causes of the global freeze as well. All of these factors contribute to the Earth’s freeze and, if left unaddressed, could have disastrous consequences for our planet.
Duration of the Earth’s Freeze
The Earth’s freeze is an annual phenomenon that occurs when the temperatures drop below freezing for an extended period of time. It is a natural occurrence that has been observed for many centuries. The duration of the freeze depends on several factors, such as the average temperature of the region, the amount of snow and ice accumulation, and the duration of sunlight exposure. Generally, the freeze can last anywhere from several days to several weeks. During this time, it is important to take precautions to ensure that all plants and animals are kept safe from the extreme cold. With a few simple steps, you can ensure that your community survives the winter freeze.
Impact of the Earth’s Freeze
The 2020 freeze has had a massive impact on the Earth’s environment and habitats. The decrease in temperature has caused a decrease in plant growth, leading to a decrease in food sources for both animals and insects. This has caused a disruption in the food chain, leading to a decrease in biodiversity, leaving some species more vulnerable than before. The decrease in temperature has also caused glaciers and sea ice to expand, leading to a rise in sea levels, flooding of coastal areas, and an increase in greenhouse gas emissions. All of this has the potential to have lasting impacts on our planet for generations to come.

Recovery from the Earth’s Freeze
The Earth’s Freeze was a global phenomenon that left the planet in a state of deep freeze. Humanity was left with a difficult task of recovering and rebuilding from the devastating effects of the freeze. Thankfully, with the help of advanced technology and a bit of ingenuity, we have managed to make strides in our recovery efforts. We have developed new methods of sustainable energy, like solar and wind, to help reduce our dependence on fossil fuels. We have also implemented new technologies such as geoengineering, which can help mitigate the impacts of climate change. Additionally, we have implemented various conservation efforts that can help protect our planet’s natural resources. With all of these efforts, humanity is slowly but surely recovering from the Earth’s Freeze and can look forward to a brighter future.
Theories Surrounding the Earth’s Freeze
Theories Surrounding the Earth’s Freeze is an intriguing topic that has been explored for centuries. While the exact cause of the freeze is still unknown, many theories have been proposed to explain the phenomenon. One popular theory suggests that the Earth experienced a sudden drop in temperature due to a change in the Earth’s orbit. Another popular theory is that the Earth experienced a rapid, large-scale cooling due to a decrease in the Sun’s energy output. Other theories suggest that the Earth experienced a global cooling event due to an increase in atmospheric dust, or a decrease in the Earth’s greenhouse gases. No matter the cause, the result was a dramatic and long-lasting freeze that changed the Earth’s climate. Through further study and research, we can continue to explore this fascinating topic and gain more insight into its potential causes.
Ongoing Effects of the Earth’s Freeze
The earth’s freeze has had a lasting and far-reaching impact on our planet. From the disruption of wildlife habitats to the effects it has had on global weather patterns, the earth’s freeze has disrupted the delicate balance of our environment. Many species of animals have been affected, as they struggle to adapt to the changing temperatures and altered landscapes. In addition, the changes in weather patterns have impacted our daily lives. With more extreme weather events occurring, we are seeing stronger storms, increased flooding, and more intense droughts. The earth’s freeze has also caused a rise in sea levels, resulting in coastal erosion, flooding, and other damaging effects. In short, the ongoing effects of the earth’s freeze are far reaching and have a lasting impact on our environment, wildlife, and daily lives.
FAQs About the How Long Did The Earth Freeze?
Q1: How long did the Earth freeze during the Ice Age?
A1: The Earth froze for roughly 2.5 million years during the most recent Ice Age.
Q2: What caused the Earth to freeze during the Ice Age?
A2: The Earth froze due to a combination of several factors, including changes in the Earth’s orbit, volcanic activity, and the decrease in greenhouse gas concentrations.
Q3: What was the impact of the Earth’s freezing during the Ice Age?
A3: The freezing of the Earth during the Ice Age had a major impact on the environment and the development of human civilization. It caused a shift in sea levels, a decrease in global temperatures, and an increase in the severity and frequency of storms.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Earth experienced periods of extreme cooling throughout its history, with the most extreme freeze occurring approximately 700 million years ago. This freeze lasted between 20 and 40 million years, making it one of the longest freezes in Earth’s history. Despite this, the Earth is now much warmer than it was during the freeze, due to the presence of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere.