How Information Being Transmitted Back to Earth
There is a lot of information being transmitted back to Earth. Some of it is from our own planet, and some of it is from other planets in our solar system. This information helps us understand our place in the universe and how we can better care for our home planet.
Nasa Astronaut Returns With Terrifying Information About Earth
The exploration of space has always been an exciting endeavor. The idea that we can learn about and explore the universe beyond our planet is both fascinating and inspiring. One of the key components of space exploration is the transmission of information back to Earth.
This process begins with data collection by satellites and other spacecraft. This data is then transmitted back to ground stations on Earth where it can be analyzed by scientists. The process of transmitting this data back to Earth can be challenging, as there can be a significant delay depending on the distance between the spacecraft and Earth.
However, despite these challenges, transmitting information back to Earth is essential for continued space exploration. It allows us to learn about the universe beyond our planet and further our understanding of the cosmos.
Why is Data Sent Digitally from Space Probes Instead of Using an Analog Device?
As digital devices become more and more prevalent in our everyday lives, it’s no surprise that they are also being used for space exploration. There are several reasons why data is sent digitally from space probes instead of using an analog device. One reason is that digital devices are much more accurate than analog devices.
When you’re dealing with something as vast and complicated as space, accuracy is crucial. With digital devices, you can be confident that the data you’re receiving is exactly what was sent – there’s no room for error. Another reason is that digital devices are much easier to store and access than analog devices.
Once the data has been digitized, it can be stored on a computer or other type of storage device. This makes it easy to share with other scientists and researchers who can then analyze it and draw their own conclusions. Finally, digital devices allow for real-time communication with space probes.
With analog devices, data would have to be recorded first and then transmitted back to Earth – which could take days, weeks, or even longer depending on the distance involved. But with digital devices, the data can be transmitted immediately, meaning we can get information about what’s happening in space in near-real time!
Credit: maxpolyakov.com
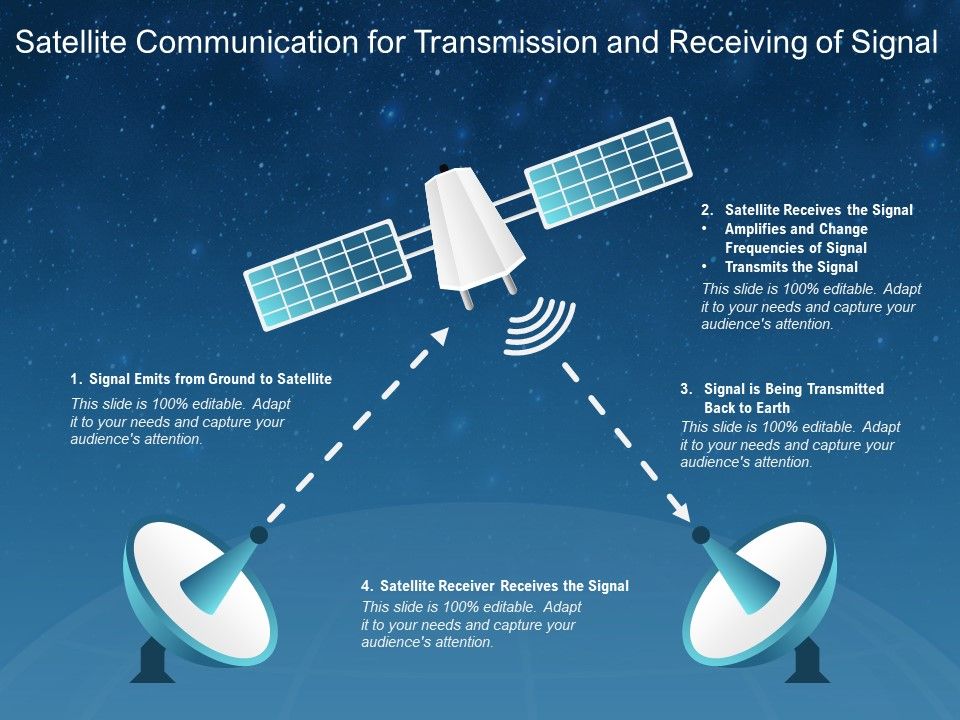
How is Information Transmitted Back to Earth?
In order to transmit information back to Earth, a spacecraft needs to have a means of communication, typically via radio waves. The spacecraft sends out a signal that is received by antennas on Earth. The strength of the signal can be used to determine how far away the spacecraft is and also allows for data transmission.
The speed of light is the limiting factor in how quickly information can be transmitted back to Earth. For example, if a spacecraft is 10 light seconds away from Earth, it will take 10 seconds for a signal to reach us. This delay must be taken into account when sending commands to a spacecraft, as they may not be able to execute them immediately.
There are various ways in which data can be encoded in a signal so that it can be transmitted back to Earth. One common method is known as Pulse Code Modulation (PCM), which essentially converts digital data into an analog signal that can be sent via radio waves. Once the signal reaches Earth, it can then be converted back into digital form so that the original data can be recovered.
How is Data Transmitted from Space to Earth?
Data is transmitted from space to Earth in a variety of ways, depending on the type of data and the spacecraft involved. For example, most images from NASA spacecraft are downlinked using radio waves at frequencies between 400 MHz and 8 GHz. The data is then typically stored on board the spacecraft until it can be downloaded during a ground station pass.
Some types of data, like real-time telemetry, are downlinked continuously as they are generated by the spacecraft.
How Do We Communicate With Earth?
There are many ways that we communicate with Earth. The most common way is through the use of satellites. Satellites allow us to send and receive information from anywhere on the planet.
They are also used to relay information between ground stations and spacecraft. Another way that we communicate with Earth is through the use of radio waves. Radio waves can be used to transmit information over long distances.
They are also used to communicate with spacecraft that are not in line of sight of a ground station. yet another popular method for communicating with Earth is via optical communication or lasers. Lasers can be used to transmit large amounts of data very quickly over short distances.
They are often used to communicate with spacecraft that are in low Earth orbit or geostationary orbit.
How Did the Astronauts Communicate With Each Other And People Back on Earth?
The Apollo astronauts communicated with people back on Earth using a variety of methods. The most common method was through voice communication, which was made possible by the use of radio equipment onboard the spacecraft and on the ground. The astronauts also used other methods of communication, such as teletype and television.
Conclusion
The blog post discusses how information is transmitted back to Earth from space. It explains that there are two ways to transmit data: through a radio wave or through a laser. Radio waves are the most common method, but they are limited in bandwidth and can be interrupted by atmospheric conditions.
Lasers offer higher bandwidth and are not affected by atmospheric conditions, but they require a clear line of sight between the transmitting and receiving antennas.






