How Does The Earth Stay Suspended In Space?
The Earth is held in place by the force of gravity. Gravity is the force that attracts two objects to each other. This force is created by the mass of the object. The more mass an object has, the greater the force of its gravity. The Earth’s mass is large enough to give it a gravitational pull that keeps it in place in its orbit around the sun. Without this pull, the Earth would drift away into space.
The Basic Laws of Physics
The laws of physics are among the most fundamental and universal of scientific principles. According to the basic laws of physics, the Earth is held in space by a combination of forces such as gravity and inertia. Gravity is an attractive force that pulls objects toward each other, while inertia is a property of matter that causes it to remain in motion unless acted upon by an external force.
These two forces work together to keep the Earth in its orbit around the sun. The gravitational pull of the sun and other objects in the solar system cause the Earth to orbit, while inertia helps to keep the Earth in its predetermined path. In addition, the Earth is constantly being pulled back toward the sun by the gravitational force, which counteracts the inertia and helps to ensure the Earth remains in its orbit.
The combination of these two forces also keeps the Earth spinning in a counterclockwise direction on its axis. The centrifugal force of the Earth’s rotation is balanced by the gravitational force of the sun and other objects in the solar system. This balance of forces helps to maintain the Earth’s axis of rotation, which is essential for the Earth’s day-night cycle.
In conclusion, the Earth is held in space by the combination of gravity and inertia, which are fundamental principles of physics. These two forces work together to keep the Earth in its orbit around the sun and spinning in a counterclockwise direction on its axis. The balance of these forces is essential to maintaining the Earth’s day-night cycle and to keeping it suspended in space.
The Earth’s Role in the Solar System
The Earth plays a crucial role in the Solar System, being the only known planet with the right conditions to sustain life. But how does a planet so large and massive stay suspended in space? The answer lies in the force of gravity. Gravitational forces exerted by the Sun and other planets keep the Earth in its current orbit, preventing it from flying off into the unknown. But this isn’t the only factor contributing to the Earth’s stability. The planet’s own angular momentum and the centrifugal force caused by its rotation help to balance the pull of gravity. Additionally, the moon’s gravity works in tandem with the Sun’s to keep the Earth in a stable orbit. All of these factors work together to keep the Earth in its place, allowing us to exist on this planet and explore the mysteries of the universe.
The Earth’s Orbit Around the Sun
Have you ever wondered how the Earth stays suspended in space? The answer lies in the Earth’s orbit around the Sun. The Earth is part of a system of planets that all revolve around the Sun in an elliptical path. This system is known as the Solar System. The Earth is held in this orbit by the gravitational pull of the Sun. The gravitational force between the Earth and the Sun is what keeps the Earth in its orbit. This force is also what causes the Earth to rotate on its axis, giving us day and night. The Earth’s orbit is affected by the gravitational pull of the other planets in the Solar System, as well as by the Sun’s magnetic field. This keeps the Earth in a stable orbit around the Sun, and helps to explain why we have seasons. So, the next time you look up at the night sky and wonder how the Earth stays suspended in space, you will know that the answer lies in the Earth’s orbit around the Sun.
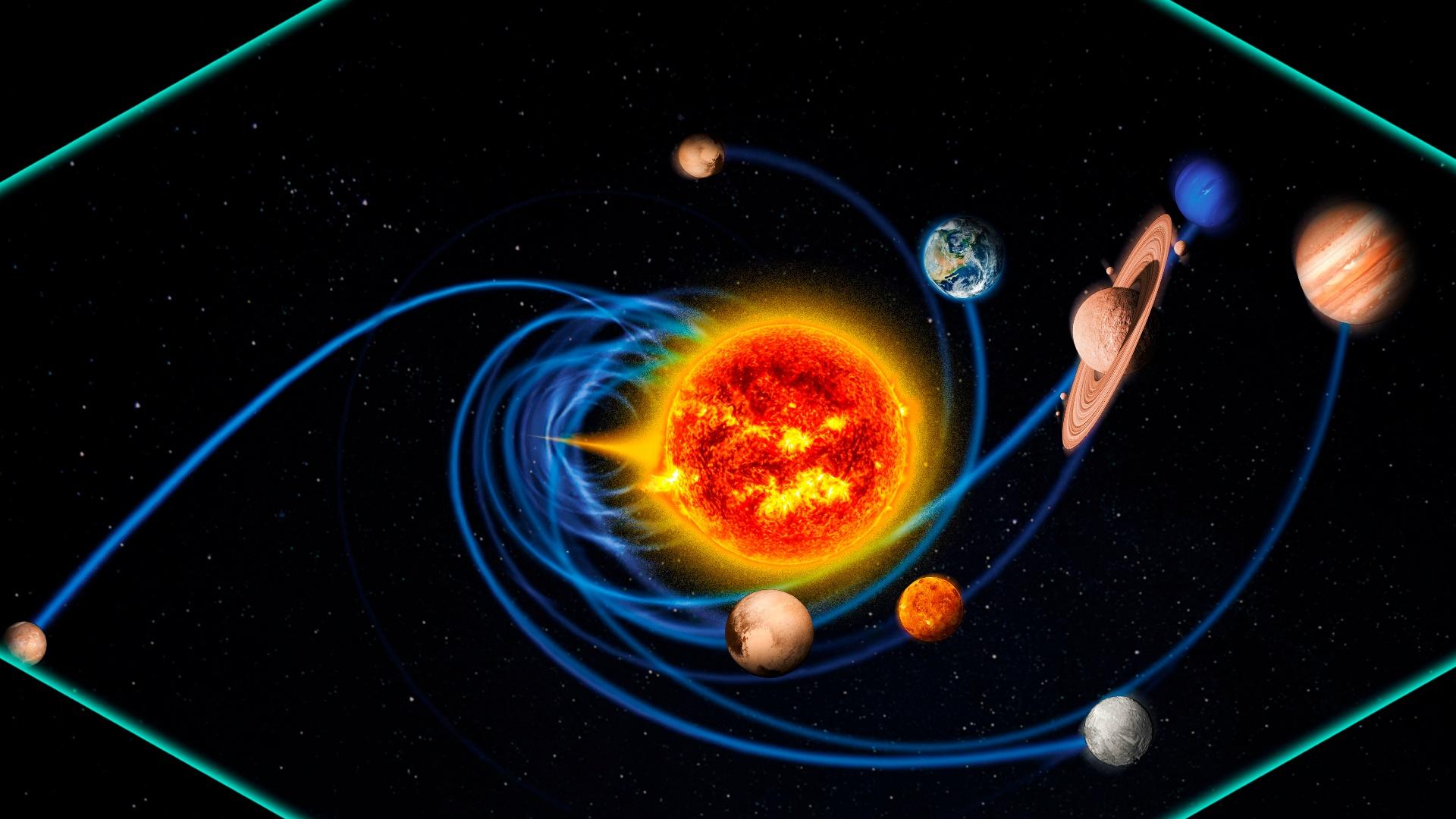
The Force of Gravity
The force of gravity is one of the most fundamental forces of nature and is the reason why the Earth stays suspended in space. It is a non-contact force that attracts any two objects with mass and keeps them together. On Earth, the force of gravity is what causes objects to fall to the ground when dropped and what keeps them attached to the ground when placed on it. In space, gravity is what causes the Earth to remain in its orbit around the Sun and what keeps the Moon orbiting around the Earth.
Gravity is the result of a fundamental property of matter known as mass. The more mass an object has, the greater the force of gravity it exerts. This means that the Earth, with its large mass, exerts a much greater force of gravity than the Moon, which has a much smaller mass. This is why the Earth remains suspended in space and why the Moon is able to orbit around it.
The force of gravity is also what makes it possible for people to walk on the ground and for objects to remain suspended in the air. Without gravity, it would be impossible for us to stay on the ground or for objects like airplanes to fly in the sky.
All in all, the force of gravity is an incredibly powerful force and is what keeps the Earth suspended in space. It is a fundamental property of matter and is what makes it possible for us to experience the world as we know it.
The Force of Centripetal Acceleration
Have you ever wondered how the Earth is able to stay suspended in space? There are a number of factors that contribute to the Earth’s orbit, one of which is the force of centripetal acceleration. The force of centripetal acceleration is the force that is responsible for the Earth’s movement around the Sun and its ability to stay in its orbital path. It works by creating a centripetal force that is directed towards the center of the orbit. This force is created by the Sun’s gravitational pull and is constantly adjusting to the changing position of the Earth in its orbit.
The force of centripetal acceleration keeps the Earth in its orbital path by counteracting the centrifugal forces that tend to push the Earth away from its orbit. This centripetal force helps to maintain the balance between the forward and backward motion of the Earth’s orbit around the Sun. Additionally, this centripetal force also helps to regulate the speed of the Earth as it moves around the Sun in its orbit. As the planet moves around the Sun, the force of centripetal acceleration keeps the planet in its orbital path and prevents it from drifting away.
In summary, the force of centripetal acceleration plays a vital role in keeping the Earth suspended in space. It is this force that creates the centripetal force that is directed towards the center of the orbit and helps to maintain the balance between the forward and backward motion of the Earth’s orbit around the Sun. Additionally, it also helps to regulate the speed of the Earth as it moves around the Sun in its orbit.
The Effects of Other Forces on Earth’s Position in Space
Earth’s position in space is not solely dependent on gravity. In addition to the force of gravity, other forces also contribute to the planet’s position in the universe. These include the centrifugal force, which is the force created by the planet’s rotational motion, and the Coriolis force, which is caused by the planet’s revolution around the sun. Both of these forces have an effect on Earth’s position in space.
The centrifugal force works by creating an outward force that is caused by the planet’s rotation. This force pushes against the force of gravity, and helps keep the planet in its place. The Coriolis force also works against gravity, and is caused by the planet’s motion around the sun. This force causes the air to move in a curved path, which helps keep the Earth in its position.
In addition to these two forces, the moon and other heavenly bodies also exert forces on the Earth, which can affect its position in space. The moon’s gravitational pull, for example, can affect the Earth’s orbit around the sun and create tidal forces. These forces can cause the planet to move slightly away from its normal position in space, which can cause changes in the planet’s climate.
Overall, the Earth’s position in space is a result of many different forces. Gravity is just one of these forces, but the other forces, such as the centrifugal force, the Coriolis force, and the lunar gravitational pull, all play a role in keeping the Earth suspended in space.
FAQs About the How Does The Earth Stay Suspended In Space?
Q: How do the forces of gravity and inertia keep the Earth in space?
A: Gravity is the force that keeps the Earth in its orbit around the Sun. Inertia is the tendency of an object at rest to remain at rest or an object in motion to remain in motion, and it helps the Earth to stay in its orbital path.
Q: What other forces are responsible for keeping the Earth in space?
A: In addition to gravity and inertia, the Earth’s spin, or angular momentum, is also responsible for keeping the Earth in its orbital path. As the Earth spins, its angular momentum works against the force of gravity to keep the Earth in its orbit and suspended in space.
Q: How does the Earth’s orbit around the Sun affect its position in space?
A: The Earth’s orbit around the Sun helps to keep it suspended in space. As the Earth moves around the Sun, its orbital velocity helps to counteract gravity and keep the Earth in its orbital path.
Conclusion
The Earth stays suspended in space due to the balance of gravitational forces that it experiences from the Sun and other large bodies in our Solar System. This combination of gravitational forces keeps the Earth in its orbit and prevents it from moving away from or closer to its source of gravity. This balance also allows the Earth to rotate around its own axis, giving us day and night. The Earth’s gravitational balance also helps to keep the atmosphere and the oceans in place, making it habitable for life.