How are the Borders of the Earth’S Tectonic Plates Defined
The Earth’s tectonic plates are constantly moving and shifting. The borders of the plates are defined by the movement of the lithosphere, which is the solid outer layer of the Earth. The lithosphere is broken into several large pieces, called plates.
These plates move on the Earth’s surface and interact with each other. The plate boundaries are where two plates meet.
The Earth’s tectonic plates are constantly moving, shifting, and interacting with each other. The borders between the plates are constantly changing as well, which can create Earthquakes and volcanoes. The Earth’s plates are defined by their chemical composition, age, and their location in relation to the planet’s hot spots.
How Do Tectonic Plates Move
Tectonic plates are the large, flat pieces of Earth’s lithosphere that make up the planet’s surface. The Earth’s lithosphere is divided into several large tectonic plates that move around on the planet’s surface. Earthquakes happen when two plates collide.
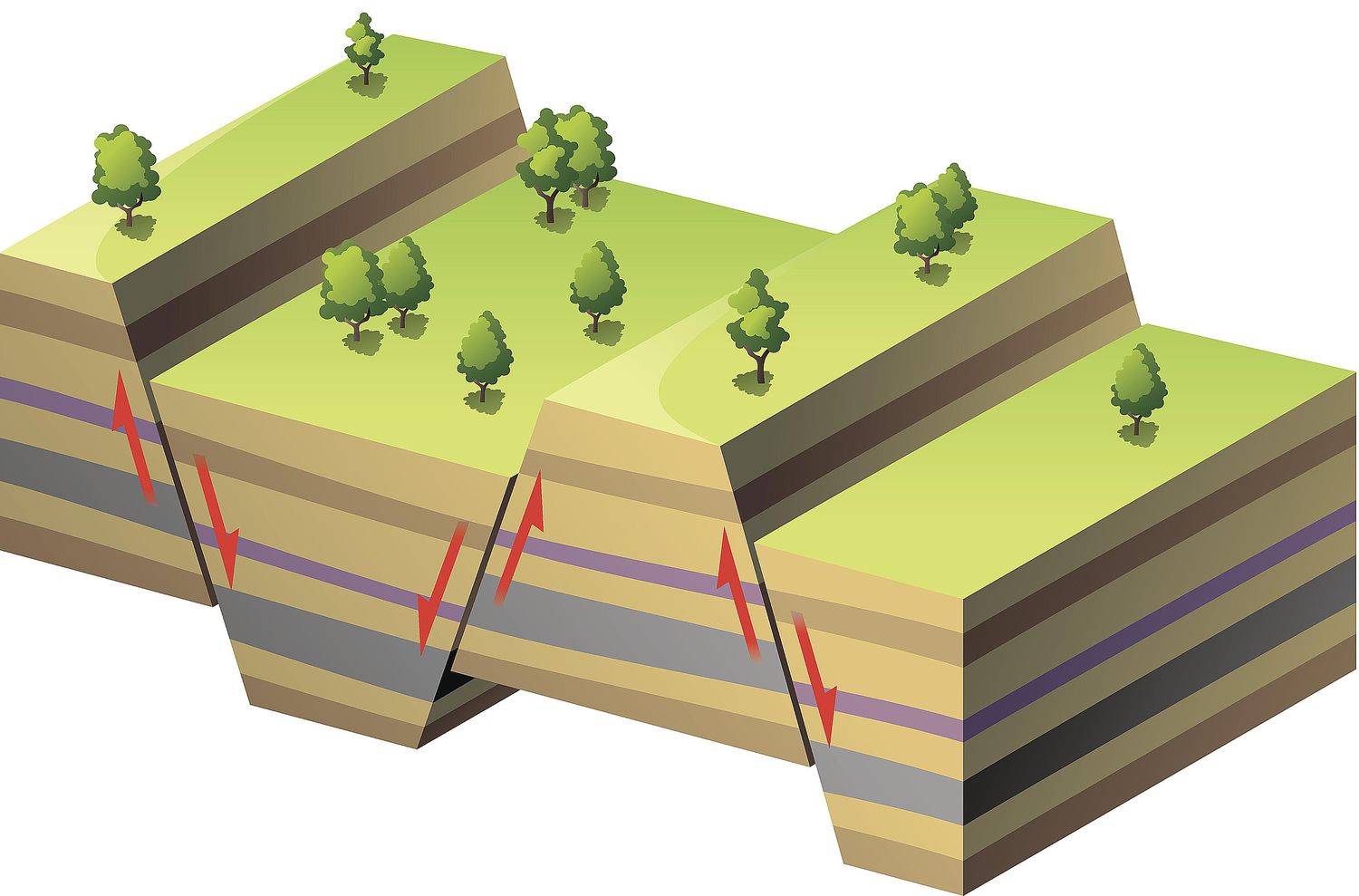
The force of the collision creates an earthquake. Plate tectonics is the scientific study of how these plates move and interact with each other. There are three main types of plate boundaries: divergent, convergent, and transform.
Divergent boundaries occur when two plates move away from each other. This type of boundary is found at mid-oceanic ridges, where new oceanic crust is being created. Convergent boundaries occur when two plates come together.
This type of boundary can be either destructive or constructive, depending on the type of crust involved. If two pieces of continental crust collide, they will crumple and form mountains (destructive). If one piece of continental crust collides with an oceanic plate, the denser oceanic plate will sink beneath the continental plate and be recycled back into the mantle (constructive).
Transform boundaries occur when two plates slide past each other horizontally without creating or destroying any crust.

Credit: www.britannica.com
How are Plate Tectonics Boundaries Identified?
Plate tectonics boundaries are identified by their location in relation to the Earth’s major plateaus. The Himalayan Plateau, for example, is located at the boundary between the Eurasian and Indian plates. The Andes Mountains, meanwhile, mark the border between the South American and Nazca plates.
Earthquakes and volcanoes often occur at plate tectonics boundaries as a result of the immense pressure that these landforms experience.
What is the Definition of a Tectonic Plate Boundary?
A tectonic plate boundary is a line where two tectonic plates meet. Tectonic plates are the huge, flat pieces of Earth’s lithosphere. The lithosphere is the outermost solid layer of Earth, which includes the crust and the upper mantle.
Tectonic plates move on Earth’s surface and interact with each other at their boundaries. There are three main types of plate boundaries:
- Divergent boundaries – also known as constructive boundaries – occur when two plates are moving away from each other. An example of this is the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, where the North American Plate and the Eurasian Plate are moving apart. As these plates move apart, the molten rock rises up from Earth’s mantle to fill in the space between them. This molten rock then cools and hardens to form a new crust.
- Convergent boundaries – also known as destructive boundaries – occur when two plates are moving toward each other and colliding with each other. An example of this is the Pacific Ring of Fire, where the Pacific Plate is subducting (or being pushed underneath) several other smaller tectonic plates such as the Philippine Sea Plate, Japanese Islands Plate, and more. When two convergent plates collide, one plate will often slide underneath (subduct)the other due to its greater density. The heavier plate then sinks down into Earth’s mantle while the lighter plate is forced upwards creating mountains or volcanoes.
- Transform fault boundaries – also known as conservative boundaries – occur when two plates are sliding past each other horizontally without any vertical movement. The San Andreas Fault in California is an example of a transform fault boundary between the Pacific Plate and North American Plate; these two massive tectonic plates grind past each other in opposite directions but neither one subducts nor pushes up over the top of one other.
The 4 Tectonic Plate Boundaries and the Hazards They Create
Conclusion
The Earth’s tectonic plates are constantly moving and shifting. The borders of these plates are defined by the boundaries between the lithosphere (the solid outer layer of the Earth) and the mantle (the hot, dense layer below the lithosphere). These boundaries are called fault lines. Earthquakes happen when two plates collide and grind against each other.