Example Of An Outlier In The Real World
An outlier is an observation that appears far away and diverges from an overall pattern in a sample. Outliers can occur by chance in any distribution, but they often indicate either measurement error or that the population has a heavy-tailed distribution. In the real world, outliers can be found in many different areas including medical research, sports, economics, and finance. For example, a person with an unusually high IQ is an outlier in the real world. Similarly, a basketball player who can consistently make shots from the other side of the court is an outlier in their sport. In economics, a company that has higher than average returns or profits can be considered an outlier. In finance, an investor who consistently outperforms the market could be considered an outlier.
Defining an Outlier
is essential for understanding the concept in the real world. An outlier is simply an observation that appears to be far from the rest of the data points. It is usually an observation that stands out significantly from the rest of the data points. Outliers can be caused by various reasons, such as data entry errors, incorrect measurements, or even changes in the environment over time. Outliers can have a major impact on the conclusions drawn from a data set. It is therefore important to identify and analyze outliers before drawing conclusions from a data set.
When looking at real-world examples of outliers, one of the most common examples is the stock market. Many investors try to predict the future movements of a particular stock, but there is no guarantee that their predictions will be accurate. When a stock experiences an unexpected surge or drop in its price, it is often considered an outlier. Similarly, when a company experiences a sudden and unexpected increase in its profits, it could be an outlier.
Outliers can also be found in the world of healthcare. For example, if a particular patient has an unusually severe reaction to a certain medication, it may be an outlier. Similarly, if a particular disease is more prevalent in a certain population, it may be an outlier. In these cases, it is important to identify and analyze the outlier to determine what caused it and use the information to inform future decisions.
Overall, outliers can have a major impact on the conclusions drawn from a data set, so it is important to identify and analyze them before drawing conclusions. By understanding outliers, it is possible to gain insight into the underlying behavior of a data set and make more informed decisions.
Identifying Outliers
Outliers are observations that are significantly different from the rest of the data. They can be either higher or lower than the average, and can appear in any data set. In the real world, outliers can have a huge impact on the results of any analysis, so it is important to be able to identify them. But how do you know if an observation is an outlier?
One simple way to identify outliers is to look at the data and see if any points stand out from the rest. If there are any points that seem significantly higher or lower than the others, then that could indicate an outlier. In addition, it is possible to use statistical techniques to identify outliers. These techniques look for data points that are outside of the expected range, or that have a high degree of variability.
When dealing with outliers, it is important to understand the underlying cause. Outliers can be due to errors in the data, or they could be the result of real-world events that are beyond the scope of the analysis. If the outlier is due to an error, it can usually be removed from the data set. If the outlier is due to real-world events, it is important to take that into account when interpreting the results.
Ultimately, outliers can have a big impact on the results of any analysis, so it is important to be able to identify them. By looking for points that stand out from the rest of the data and using statistical techniques, it is possible to detect and understand outliers in the real world.
Causes of Outliers
An outlier is any data point that stands out from the rest of the data. While there can be several causes of outliers, the most common are errors in the data-gathering process, measurement error, or a data point that is simply an extreme value. Regardless of the cause, outliers can have a significant impact on the results of a study, and should be identified and addressed.
Errors in data-gathering processes, such as data entry errors, can lead to outliers. For example, if a data entry specialist enters the wrong data into a database, it can lead to an outlier that is not representative of the population. Measurement errors, such as incorrect readings, can also lead to outliers. Finally, extreme values can also lead to outliers. For example, a student with an exceptionally high grade in a class could be considered an outlier.
It is important to recognize and address outliers, as they can have a significant impact on the results of a study. Outliers should be identified and, if appropriate, removed from the data set. In some cases, outliers may be the result of errors in the data-gathering process or measurement errors, and should be addressed as such. In other cases, outliers may be the result of extreme values, and should be treated as such. Regardless of the cause, it is important to identify and address outliers in order to ensure the accuracy of the results.

Potential Benefits of Outliers
Outliers can provide meaningful insights into patterns and trends that would otherwise be difficult to uncover. They can also prompt us to rethink our assumptions and challenge the status quo. For example, an outlier in a data set can help identify a previously unknown market segment or customer base, thus allowing for more effective targeting of resources. Similarly, outliers can provide valuable information on how best to optimize processes or systems, resulting in greater efficiency and productivity. Additionally, understanding outliers can help us better forecast future trends and anticipate potential problems. The key is to use outliers to inform decision making, allowing for the development of multiple scenarios and the testing of hypotheses. By doing so, organizations can gain valuable insights that can be used to make informed decisions and improve operations.
Challenges of Outliers
Outliers are points or observations in a dataset that are far removed from the majority of the data. These points are extreme values, which are most likely to be errors or mistakes made during data collection. Outliers can be very difficult to identify and can significantly skew the results of an analysis if not properly handled.
In the real world, outlier examples can be found in almost any field. In the medical field, outlier patients can present with unusual symptoms or have diagnoses that are not seen in the general population. In the business world, outliers may be customers who spend significantly more or less money than other customers. In the financial world, outliers can be stocks that have drastically different returns than the rest of the market.
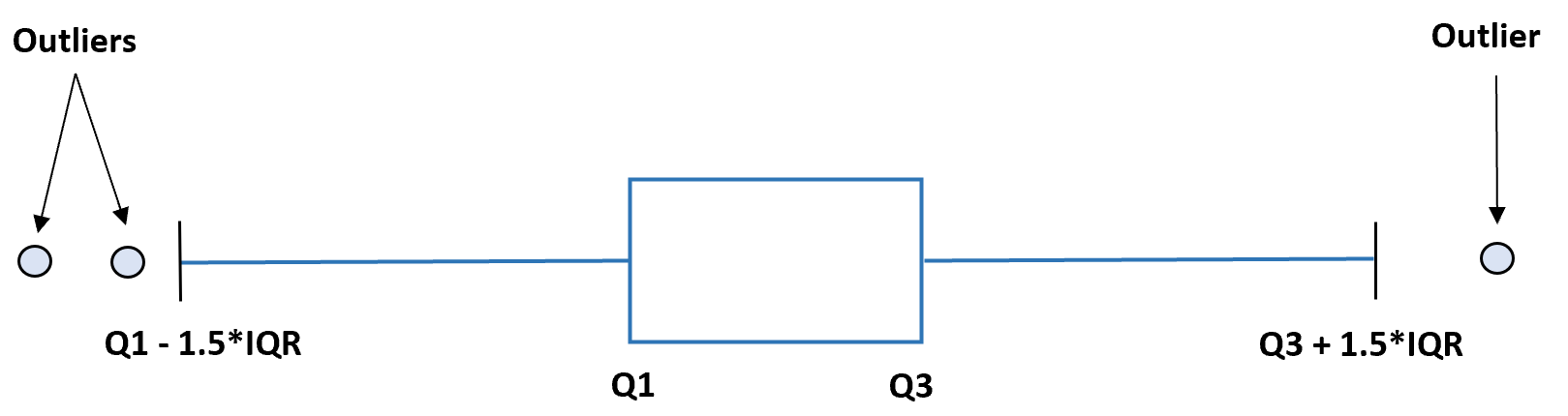
When dealing with outliers, it is important to identify them and understand why they exist. This can be done by using statistical methods, such as box plots and extreme value analysis. Once identified, outliers should be researched further to determine if they are valid observations or potential errors. If the outliers are valid, they should be included in the analysis. If they are errors, they should be removed or corrected.
Overall, outliers can present unique challenges and should be handled with care. By understanding the implications of outliers and using proper statistical methods, they can be identified and handled accordingly. This will help ensure that the data is accurate and the results of the analysis are not affected by extreme values.
Mitigating Outlier Effects
Outliers are data points that are significantly different from the rest of the data, often due to anomalies or unusual circumstances. Outliers can have a profound effect on data analysis, skewing results and potentially leading to incorrect conclusions. It is important to identify and mitigate outlier effects when conducting data analysis.
One method to mitigate outlier effects is to remove the outlier data points from the data set. This can be done by comparing data points to the mean or median of the data set. Data points that lie well outside of the range of the majority of the data points should be removed. Another approach is to switch to a more robust form of analysis, such as using medians instead of means, which are less susceptible to outliers.
In addition, to prevent outliers from affecting the results of an analysis, it is important to understand the underlying cause of the outlier. In some cases, the outlier may be caused by an anomaly in the data set or an error in the data collection process. If this is the case, it is important to identify the source of the error and correct it before proceeding.
Finally, it is important to consider the impact of an outlier on the overall data set. Outliers can have a significant effect on the results of an analysis, so it is important to understand how the outlier impacts the overall results. For example, if the outlier is responsible for a large portion of the variance in the data set, it may be necessary to remove it in order to get accurate results.
By understanding and mitigating outlier effects, data analysts can ensure that their results are accurate and that any outliers do not have a negative impact on the results.
FAQs About the Example Of An Outlier In The Real World
1. What is an example of an outlier in the real world?
An example of an outlier in the real world is someone who earns a salary higher than 99% of other individuals in their profession.
2. How can outliers affect data analysis?
Outliers can have a significant impact on data analysis, as they can skew results and lead to inaccurate conclusions.
3. How can outliers be identified?
Outliers can be identified by plotting data points on a graph or by using statistical methods such as box plots and z-scores.
Conclusion
An outlier in the real world is an example of an extreme or unusual event or occurrence that does not fit the normal pattern. Outliers can be seen in a variety of different ways, from economic trends to geographical locations. They can also occur in a variety of different areas, such as health, education, business, or any other field. Outliers are important to consider when analyzing data as they can provide valuable insight into the data being studied. By understanding outliers, researchers can better understand the reasons behind the data and uncover potential new information.