An Example Of Ricardian Model In Real World
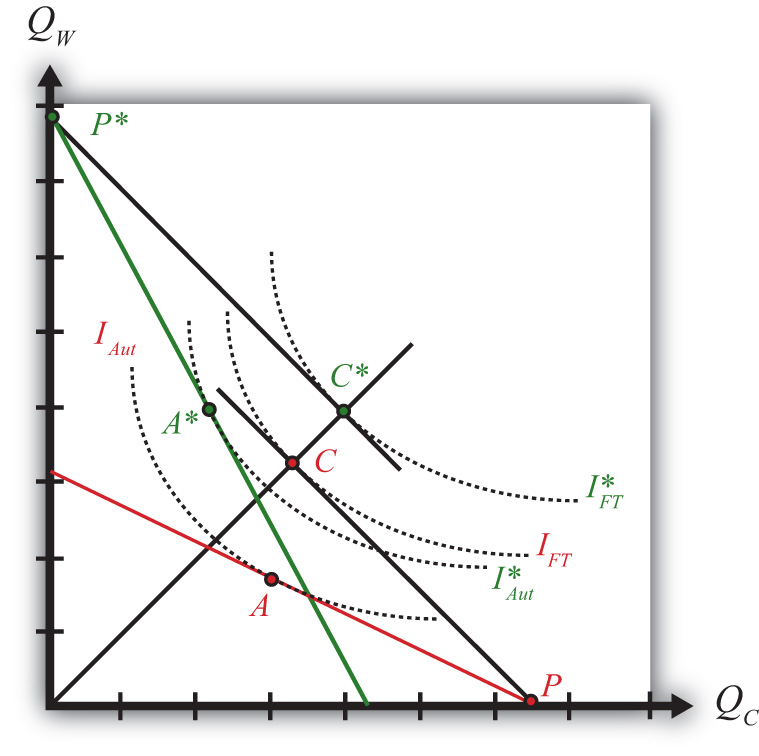
The Ricardian Model is a simple economic model that was developed by David Ricardo in 1817. It is an economic model that illustrates the relationship between the cost of production and the price of goods. The model suggests that when the cost of production increases, the price of goods will also increase. This model is often used to explain the effects of trade on the prices of goods, as well as the effects of complex international trade agreements. An example of the Ricardian Model in the real world is when a country increases its production of a certain good, making it more readily available in the market, and therefore driving down its price. This is an example of how the Ricardian Model can be used to explain the effects of production on prices.
What is the Ricardian Model?
The Ricardian Model is a theory developed by the 19th century economist David Ricardo which suggests that international trade can be beneficial to all parties involved. The theory argues that when two countries engage in free trade, both countries can benefit from comparative advantage. Comparative advantage is a concept which states that a country can produce goods at a lower cost than its trading partner, thus making it economically advantageous to specialize in certain good or service.
The Ricardian Model is often used to explain the benefits of international trade and is still relevant today. For example, the Ricardian Model can be used to explain how countries such as China can benefit from specialization in the production of certain goods and services. By focusing on the production of certain goods and services, China is able to produce those goods and services at a lower cost than its trading partners. As a result, China is able to reap the economic benefits of its comparative advantage.
The Ricardian Model can also be used to explain how countries can benefit from the exchange of goods and services. By engaging in free trade, countries can benefit from increased specializations, higher levels of production, and improved standards of living. Additionally, free trade can lead to lower prices for consumers and improved economic growth.
In short, the Ricardian Model is an important economic concept which explains the benefits of international trade. The model suggests that countries can benefit from specialization in certain goods and services and from the exchange of goods and services. By understanding the Ricardian Model, countries can gain insight into how to reap the benefits of international trade.
How the Ricardian Model is Applied in the Real World?
The Ricardian Model is a classical theory of international trade developed by David Ricardo in the 19th century. It suggests that countries should specialize in production of goods in which they have a comparative advantage and then trade with other countries for goods in which they have a comparative disadvantage. This model has been applied to the real world to explain how countries benefit from international trade.
In the Ricardian Model, countries specialize in producing goods they are best at producing, such as agricultural products, manufactured goods, or services. When countries specialize, the labor and capital resources used are more productive and efficient than if the same resources were used to produce a variety of goods. This specialization increases productivity and lowers costs, allowing countries to export goods at cheaper prices than if they were to produce all goods domestically.
The Ricardian Model also suggests that countries should specialize in goods in which they have a comparative advantage. This means that a country should produce goods in which it can produce more efficiently than other countries. This is based on the idea that countries can benefit from specializing in goods in which they have a comparative advantage, rather than producing a variety of goods in which they have no comparative advantage.
The Ricardian Model has been used to explain the benefits of international trade and has been used to explain why countries specialize in the production of certain goods. The model has been used to explain the benefits of trade agreements, the effects of tariffs, and the effects of trade liberalization. In the real world, the Ricardian Model has been used to explain the economic benefits that countries gain from engaging in international trade.
Benefits of Using the Ricardian Model
The Ricardian Model is a powerful tool for assessing the effects of international trade on a country’s economy. The model is used to calculate the gains from trade by considering the costs of production, the terms of trade, and the distribution of resources. In addition to providing an accurate assessment of the impact of trade, the model can also be used to identify potential gains and opportunities for growth. By understanding the benefits of using the Ricardian Model, businesses can make informed decisions about their international trade activities.
The Ricardian Model provides a number of advantages for businesses. First, it allows businesses to better understand the potential gains from international trade. By understanding the full costs of production and the terms of trade, businesses can make more informed decisions about their international activities. Second, the Ricardian Model can also be used to identify potential gains and opportunities for growth. By understanding the terms of trade and the resources available, businesses can identify potential areas of growth and potential areas for improvement. Finally, the Ricardian Model can be used to compare the benefits of different countries and different markets. By understanding the terms of trade and the resources available, businesses can better assess the potential gains from international trade.
Overall, the Ricardian Model offers a powerful tool for businesses to assess the potential gains from international trade. By understanding the costs of production, the terms of trade, and the resources available, businesses can better understand the potential gains from international trade. Utilizing the model can also help businesses identify potential areas of growth and potential areas for improvement. Understanding the potential gains from international trade can help businesses make informed decisions about their international activities.
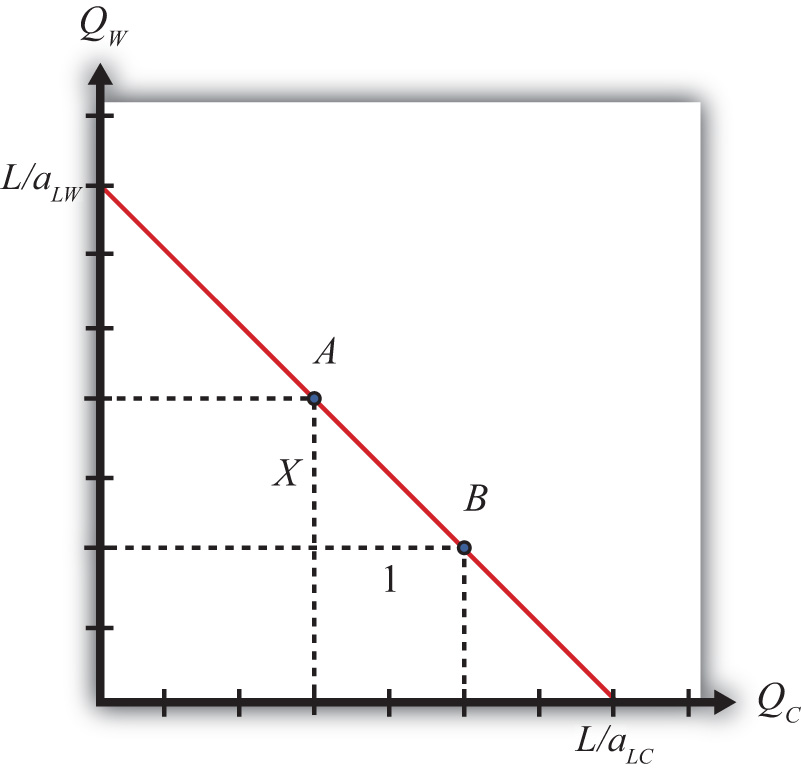
Challenges of Implementing the Ricardian Model
The Ricardian Model is a powerful tool for analyzing the economic effects of international trade, but it does come with certain challenges. Implementing the model requires specialized knowledge of economic theory and complex data analysis. Additionally, the Ricardian Model does not account for the effects of government policies or other external factors, which can greatly influence economic outcomes. Furthermore, Ricardian Model relies on assumptions about preferences, which can be difficult to evaluate in a real-world setting.
Despite these challenges, the Ricardian Model is still widely used in economics. By providing a clear framework for understanding international trade, the Ricardian Model has proven to be an invaluable tool in many real-world applications. For example, it has been used to analyze the effects of different trade agreements and to assess the impact of tariffs on international markets. In addition, the model can be used to develop strategies for mitigating the negative effects of international trade.
Overall, the Ricardian Model offers a valuable framework for understanding the economic effects of international trade. Despite its challenges, the model has proven to be an effective tool for analyzing real-world economic scenarios. By understanding the challenges of implementing the Ricardian Model, economists can develop strategies to make the most of its potential in real-world applications.
Examples of the Ricardian Model in Action
The Ricardian Model is a classic economic theory, first proposed by 19th-century British economist David Ricardo, that illustrates the benefits of free trade among countries. The Ricardian Model suggests that countries should specialize in producing those goods that they can produce more efficiently than their trading partners, and then trade with each other to take advantage of the comparative advantages in production. While the Ricardian Model is a useful conceptual tool, it is also possible to see examples of it in action in the real world.
Take the example of the United States and China. The US has a comparative advantage in producing high-value goods such as aircraft and medical equipment, while China has a comparative advantage in producing low-value but labor-intensive products such as textiles and footwear. By trading with each other, both countries take advantage of their respective comparative advantages and benefit from increased efficiency and cost savings.
Another example of the Ricardian Model in action can be seen in the automotive industry, where different countries specialize in producing certain components. For example, Japan is renowned for producing high-quality automotive engines, while Mexico is known for its manufacturing expertise in producing parts such as suspension systems and exhausts. By trading with each other, these countries can take advantage of their respective specializations and produce cars with superior quality and lower costs.
These are some of the examples of how the Ricardian Model works in practice. By understanding the benefits of specialization and free trade, countries are able to produce and consume goods in a more cost-effective and efficient manner.
Summary and Conclusion
The Ricardian Model is a classic economic framework that helps economists better understand the effects of trade between two countries. It is based on the idea that each country gains from international trade when the production of goods and services is more efficient in one country than in the other. As demonstrated through an example, this model is still relevant in the modern world.
The example shows that at the heart of the Ricardian Model is the concept of comparative advantage. This means that it is beneficial for a country to focus on producing the goods and services that it has a competitive edge in, as this will result in a more efficient overall allocation of resources. This is true both in terms of labor and capital, as countries can specialize in producing the goods and services that are most suited to their resources.
The Ricardian Model is also an important tool for understanding the effects of free trade. In the example, it is clear that both countries can benefit from trading with one another, as each country has something to offer the other. This example shows that the Ricardian Model can be used to inform real-world trade decisions, as it provides an understanding of how trade can be beneficial to both parties.
In summary, the Ricardian Model is a classic economic framework that helps economists better understand the effects of trade between two countries. It is based on the idea of comparative advantage, and is still relevant in the modern world. This example shows that the model can be used to inform real-world trade decisions, as it provides an understanding of how trade can be beneficial to both parties.
FAQs About the An Example Of Ricardian Model In Real World
Q1: What is the Ricardian Model?
A1: The Ricardian Model is an economic model that was developed by David Ricardo in the early 19th century. It is based on the theory of comparative advantage which states that different countries should specialize in the production of goods and services that they have a comparative advantage in.
Q2: What is an example of the Ricardian Model in the real world?
A2: One example of the Ricardian Model in the real world is the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA). NAFTA is an agreement between Canada, the United States, and Mexico that allows for the free flow of goods and services between the three countries. NAFTA is based on the principles of comparative advantage and has led to increased economic growth in all three countries.
Q3: How does the Ricardian Model affect international trade?
A3: The Ricardian Model has had a significant impact on international trade. By allowing countries to specialize in the production of goods and services that they have a comparative advantage in, the Ricardian Model has made trade between countries more efficient and has increased global economic growth.
Conclusion
The Ricardian Model of international trade is an example of the classical economic tradition. It has become an important tool for understanding the effects of international competition and the implications of different trade policies. In the real world, the Ricardian Model has been used to analyze the effects of trade liberalization, the impact of changing exchange rates, and the economic effects of changes in tariffs and other barriers to trade. While the model is not perfect, it provides a useful framework for understanding the effects of international trade.