1 Real World Example Of An Earthquake
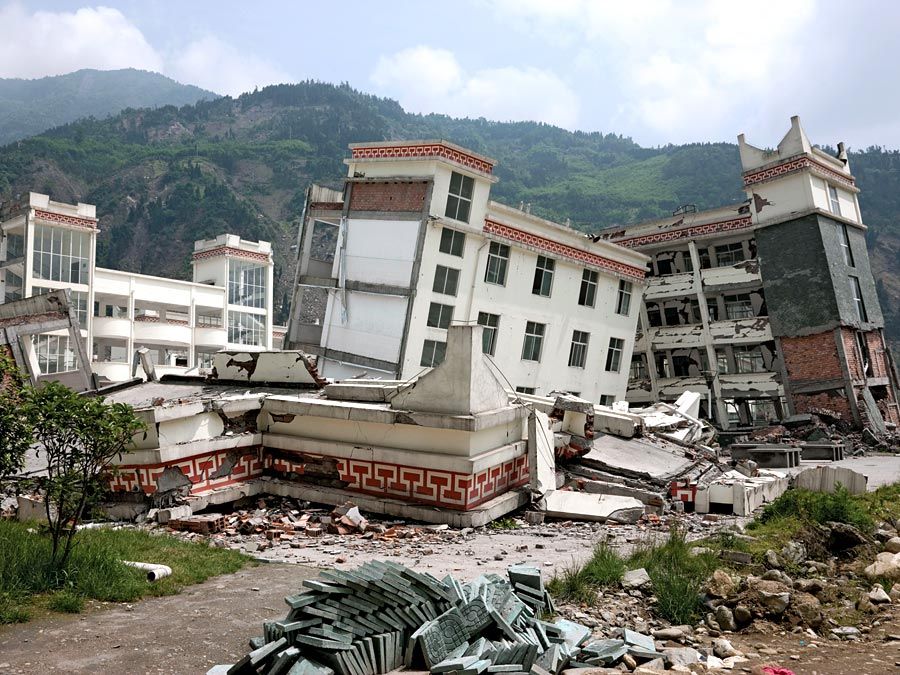
An example of a real-world earthquake is the 2010 Chile Earthquake. This magnitude 8.8 earthquake struck off the coast of central Chile on February 27, 2010, resulting in substantial damage and loss of life. The quake was felt in many parts of the country, with the epicenter located near the city of Concepción. The quake caused a tsunami that affected several countries in the Pacific, including Hawaii, Japan, and New Zealand. In Chile, the earthquake caused extensive structural damage, with a total of 521 deaths and over 1 million people displaced. It was the sixth strongest earthquake ever recorded.
Definition of An Earthquake
Earthquakes are one of the most destructive forces of nature, and they can cause extensive damage to property and lives. An earthquake is a sudden and violent shaking of the ground, caused by the rapid release of energy from the Earth’s crust. Earthquakes occur when two blocks of the Earth’s lithosphere (the crust and uppermost mantle) suddenly slip past each other. The energy released creates seismic waves that can travel through the Earth’s crust and cause the ground to shake. Earthquakes can range in intensity from barely noticeable tremors to destructive quakes that can level cities. As the seismic waves from an earthquake move outward, they cause the ground to shake, and can also cause landslides, tsunamis, and other disasters.
Earthquakes can occur in any part of the world, but they are most common along major plate boundaries. The majority of earthquakes happen along the Ring of Fire, a zone of seismic activity that circles the Pacific Ocean. Earthquakes are measured using the Richter scale, which assigns a magnitude to each quake based on the amount of energy released. Earthquakes with a magnitude of 5.0 or greater are considered to be strong, and those with a magnitude of 7.0 or greater can cause considerable damage.
In conclusion, an earthquake is a sudden and violent shaking of the ground, caused by the rapid release of energy from the Earth’s crust. Earthquakes can range in intensity from barely noticeable tremors to destructive quakes that can level cities. Most earthquakes occur along the Ring of Fire, and they are measured using the Richter scale. Understanding the nature of earthquakes is essential to being able to prepare for and mitigate the effects of a quake.
Causes of An Earthquake
Earthquakes are caused by the movement of tectonic plates, which are the large pieces of Earth’s crust that float on the molten mantle beneath them. Earthquakes are the result of sudden movement of these plates, usually when two of them collide. This sudden movement releases energy in the form of seismic waves, which can be felt by humans. Earthquakes can also be caused by volcanic activity, when magma and other molten materials beneath the Earth’s surface are released. Earthquakes are most commonly associated with faults, or cracks in the Earth’s surface, where two plates have collided and are stuck together. When the tension between the two plates reaches a breaking point, the plates slip past each other and release the energy, causing an earthquake. Earthquakes can also be caused by human activities, such as mining or the use of explosives.
Effects of An Earthquake
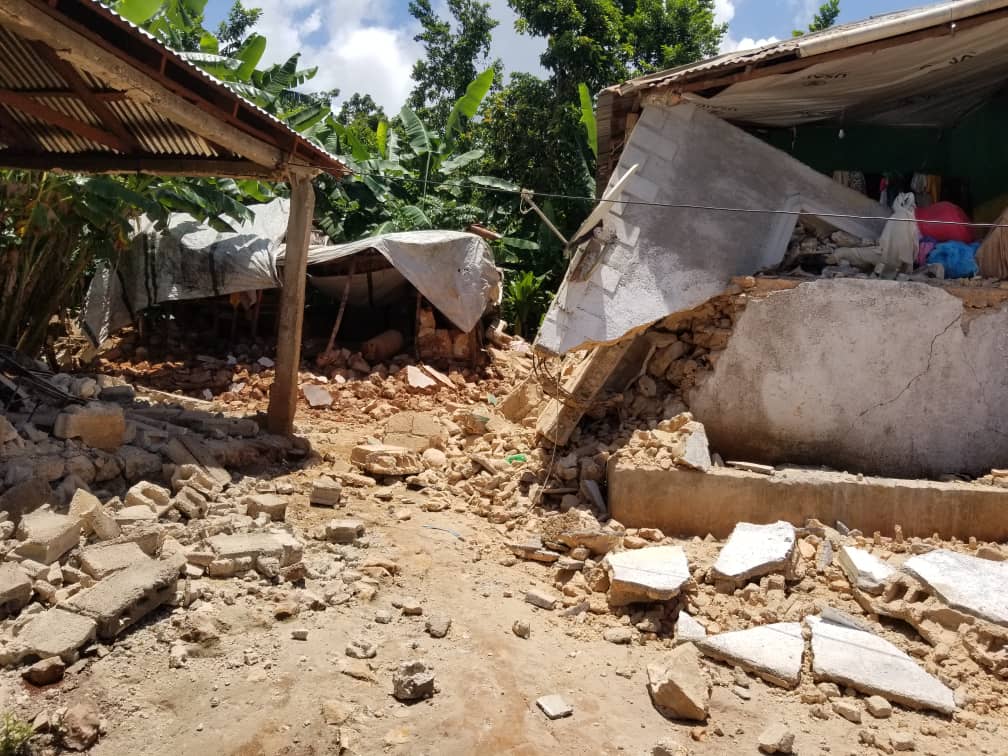
Earthquakes can cause devastating damage to property and lives, and their effects can be felt over large distances. Earthquakes are caused when two tectonic plates move past each other and cause the ground to shake, resulting in the release of energy in the form of seismic waves. An example of an earthquake is the one that occurred in Haiti in 2010, which killed over 200,000 people and affected millions. It caused widespread destruction of infrastructure, including roads, bridges, and buildings, resulting in the displacement of thousands of people. The effects of this earthquake were felt as far away as Cuba and the Dominican Republic.
The most common effects of an earthquake are tremors, landslides, floods, fires, and tsunamis. Tremors are the shaking of the ground which can be strong enough to cause significant damage to buildings and other structures. Landslides occur when the shaking of the ground causes loose rocks and soil to move, often resulting in destruction of roads, bridges, and other structures. Floods often follow earthquakes due to the destruction of infrastructure, and can result in extensive damage. Fires can also be caused by the shaking of the ground, and can spread quickly if not contained. Tsunamis are large waves created by earthquakes that can cause extensive damage to coastal areas.
Earthquakes can have long-term effects, such as disruption of the local economy, environmental damage, and psychological trauma. Earthquakes can also have a global impact, as they can cause changes in the global climate and affect the global economy. Earthquakes can also cause changes in the Earth’s crust, resulting in changes in the landscape. Therefore, it is important to be aware of the potential risks associated with an earthquake, and to be prepared for the possible effects.

History of Earthquakes
Earthquakes have been around since the dawn of time, with some of the earliest known records dating back to 1456 BC. Throughout history, earthquakes have caused significant destruction, resulting in countless deaths and displacements of people. Earthquakes are usually caused when two tectonic plates collide or grind against each other, resulting in the release of energy in the form of seismic waves. Earthquakes don’t always result in devastation, but they can still cause considerable disruption. In some regions, such as Japan and California, earthquakes are a regular occurrence. They’re also common in the Mediterranean region, including Greece and Italy. In addition, earthquakes have been known to occur in the United Kingdom, although they’re typically much smaller in magnitude. To help reduce the risk of earthquakes, it’s important to know how to prepare for them. This includes knowing how to identify the signs of an impending earthquake, such as animals behaving strangely, unusual loud noises, and the ground shaking. It’s also important to have an emergency plan in place, such as knowing where to go, and having an emergency kit or supplies ready. While preparing for an earthquake can be difficult, it’s important to be aware of the dangers and be prepared. One of the most infamous earthquakes in recent memory is the 2010 earthquake in Haiti. This magnitude 7.0 earthquake caused widespread destruction and claimed over 230,000 lives. It also left many people homeless and the country in a state of disrepair. This earthquake serves as a stark reminder of the destructive power of earthquakes and the importance of being prepared for them.
Preparing for An Earthquake
Earthquakes are one of the most destructive forces of nature and can cause significant damage to property and lives. Preparing for an earthquake is an essential step for anyone living in an area that is prone to them. Knowing what to do in the event of an earthquake, and having the necessary supplies and equipment on hand, can help you stay safe and minimize the damage.
The best way to prepare for an earthquake is to create an emergency preparedness plan. This plan should include a list of items you need to have on hand, such as food, water, flashlights, a radio, and a first-aid kit. You should also become familiar with your local emergency response plans and the evacuation routes in your area. Additionally, it is important to inspect your home for structural damage and make sure it is up-to-date with current building codes.
It is also important to practice earthquake drills with your family. This will help everyone understand what to do and where to go during an earthquake. Make sure you identify a safe spot in each room of your home, and practice getting to that spot quickly and safely.
Finally, having the right supplies and equipment on hand can help you cope with the aftermath of an earthquake. Make sure your emergency preparedness plan includes a stock of emergency supplies like canned food, water, flashlights, and batteries.
By following these steps, you can be better prepared for an earthquake and minimize the potential damage to your property and your safety.
Mitigating the Impact of An Earthquake
Earthquakes are some of the most destructive natural disasters that can occur. There are very few ways to stop an earthquake once it has started, and the only way to avoid the devastating effects of an earthquake is to mitigate the impact it can have on people and property. Here are some ways to help reduce the risk of damage from an earthquake.
First, build structures with seismic-resistant designs. This means using materials and designs that are better able to withstand the shaking from an earthquake. Additionally, earthquake-resistant building codes should be followed when building new structures.
Second, create a family emergency plan and make sure everyone in the household knows what to do if an earthquake occurs. Also, having an earthquake kit stocked with food, water, first aid supplies, and a battery-operated radio and phone charger is essential.
Third, retrofit existing buildings with earthquake-resistant features such as bracing, bolting, and reinforcing walls. Retrofitting can help reduce the risk of collapse and make buildings more resistant to earthquake shaking.
Finally, participate in local emergency drills and make sure that everyone in your household is familiar with the emergency plans.
By following these tips, individuals can help reduce the risk of damage and injury during an earthquake. While there is no way to completely prevent earthquake damage, taking the steps listed above can help minimize the impact of an earthquake on people and their property.
FAQs About the 1 Real World Example Of An Earthquake
Q1: What is a real world example of an earthquake?
A1: One example of a real-world earthquake is the 2010 Haiti earthquake which had a magnitude of 7.0.
Q2: How destructive can an earthquake be?
A2: Depending on the magnitude of the earthquake, destruction can range from minor to major. The 2010 Haiti earthquake caused widespread destruction and loss of life.
Q3: What other impacts can an earthquake have?
A3: Earthquakes can cause a variety of secondary effects including landslides, tsunamis, and fires. In addition, they can cause infrastructure damage such as power outages, communication disruptions, and transportation delays.
Conclusion
The 2010 earthquake in Chile is a real world example of an earthquake. It was the sixth largest earthquake ever recorded, with a magnitude of 8.8 on the Richter scale. The earthquake caused a tsunami that affected many coastal areas, leading to extensive damage and loss of life. This event serves as a reminder of the power and potential destruction of earthquakes, and the importance of taking steps to prepare for them.